(April 8, 2022) Gingerly, she lifted one leg onto her bicycle. Haltingly, she pedalled. All she knew around 50 years ago was she was here to serve and help the downtrodden – and Sudha Varghese went about it with dedication. Soon the “Cycle Didi” was a welcome face working tirelessly for the upliftment of the Musahars, a Mahadalit community of Bihar. The Padma Shri (2006) awardee brushes aside accolades, as for this altruistic mind, people and their plight are all that matters. Born in Kottayam, Kerala, Sudha shifted to Bihar in her late teens and saw the harsh reality of the have-nots. Today, Sudha runs several residential schools for girls and offers livelihood programmes for women, and empowers these Dalit communities from the shackles of the upper caste.
“When I came to Bihar and saw the condition of these people, I knew I had to do something, especially for women. I lived with them for years, and taught the girls in my small room,” shares the Padma Shri awardee, in an interview with Global Indian. “I devoted all my energy, time, and love to help the Musahar community,” she says. Known for their vocation of rat-catching, the Musahars lived on village fringes and faced caste and gender atrocities from the upper castes.

Sudha Varghese
Age no bar
Born into a prosperous family in 1944, the eldest of six siblings, she admits to being a pampered child. A love for the arts saw her take part in plays, dance, and singing competitions at school. “As the first child, my grandparents – maternal and paternal – loved me a lot. I liked being in nature,” she adds.
Even as a child, the plight of the impoverished concerned her. In middle school, sifting through a magazine, she chanced upon a photograph of a ramshackle hut in Bihar. “I couldn’t get that image out of my head. The thought that a family had to live in that condition made me sad,” shares the 77-year-old social worker.
Sudha Varghese with students of Prerna school
Around this time, she joined the Notre Dame Academy, and despite resistance from her family, entered the religious order to become a Catholic nun. “When I told my family that I wanted to go to Bihar, my parents refused. I tried to convince them, but they did not want to listen. One day, my maternal grandfather came home and after speaking to me, persuaded my parents to let me go,” she says.
Overcoming the challenges
Life in Bihar wasn’t easy. It took Sudha a year to understand the deep-rooted caste system, discrimination, and untouchability. However, the biggest struggle was language. “When I shifted from Kerala, I knew little English. I didn’t speak Hindi. Soon, I realised that I will have to learn both if I wanted to help the Musahar community,” she shares, adding, “I was unaware of the evils of the caste system, and the miserable state of the community – no home or income, forced to beg and live on footpaths.”
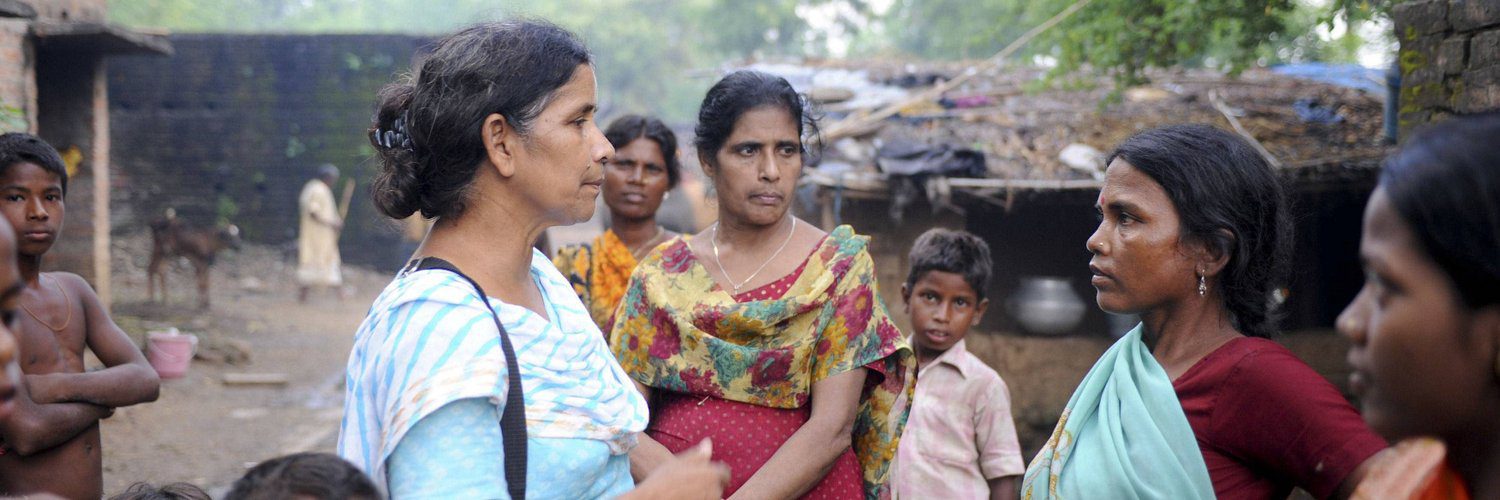

Sudha interacting with ladies of the Musahar community
At the Notre Dame Academy, unhappy that she wasn’t doing enough, she struck out on her own. She asked some Musahar villagers for a place to stay and was offered a grain shed – where she started classes for girls. “The major source of income for this community was making tadi (toddy). Customers would come to buy liquor, and that disturbed the education of young girls. So, I asked them to come to my room, where I used to take classes – not just academic, but sewing and embroidery too,” smiles the social worker.
Soon many girls started attending classes. But educating them wasn’t enough. Raising a voice for their rights and funding for hand pumps to access clean water – Sudha was unstoppable. The activist encouraged them to demand higher daily wages. That did not go down well with several people who threatened to oust her. “I had to leave my home in Danapur and shift to a rented one. There were days and nights when I feared that I could be killed. I realised that if I had to work for these people, being scared wouldn’t help. I had to stand up to them, so I went back,” smiles the social worker.
In 1987, she launched Nari Gunjan, an NGO to help Dalit women access rights. Two years later, straddled with a law degree (from a Bengaluru school) she fought cases for abused women – domestic violence and rape. “I went to the authorities initially, but later enrolled at the law school to ensure these women get justice,” she adds.
Changing mindsets
To educate Dalit girls, she slowly redefined their image – by establishing a residential school – Prerna (in the outskirts of Danapur, Patna) in 2005. “Girls were not allowed into schools. Upper castes had made it impossible for the people from Dalit and Musahar communities to survive. Even basic amenities were not provided. With funding from the state government and volunteer donations, we started the first batch in 2006,” Sudha shares, of the school which was “half public latrine and half water-buffalo shed.”
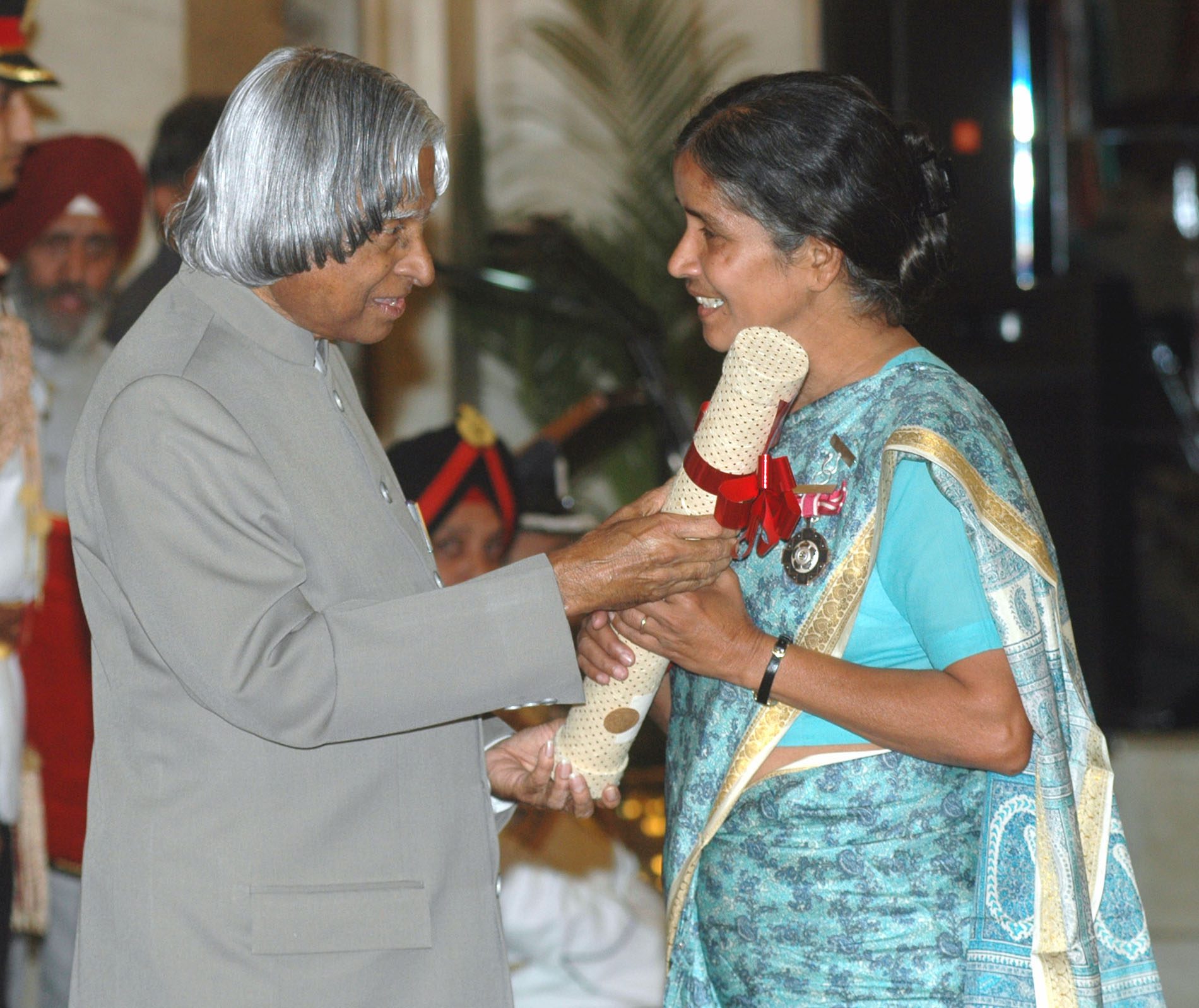

APJ Abdul Kalam presenting the Padma Shri Award (2006) to Sister Sudha Varghese in New Delhi on March 20, 2006
Her aim was not just academics, but also extracurriculars – she added karate, and the girls became so adept, they won five gold, five silver and 14 bronze medals at a competition in Gujarat (2011), winning a trip to Japan to participate at the International Martial Arts Championship organised under the auspices of Japan Shotokan Karate-Do Federation. “The girls are now pursuing their dreams – studying to become doctors, engineers, lawyers, and leaders – and that makes me happy,” she gushes.
Her initiative Nari Gunjan is active in five Bihar districts and runs empowering campaigns. “After the Nitish government put a ban on liquor, many had no income. So, we encouraged women to start a kitchen garden to grow vegetables and sell excess produce. Or make commercial chane ka sattu, which was a big hit,” says the social worker.
Another unique livelihood programme – the Nari Gunjan Sargam Mahila band, an all-women band belonging to the Devadasi Dalit community garnered much acclaim. “When we first approached them with the idea, they were unsure. We trained them, and now they perform at various government and high profile events. We are working on creating a second band now,” laughs Sudha. The NGO also produces inexpensive sanitary napkins.
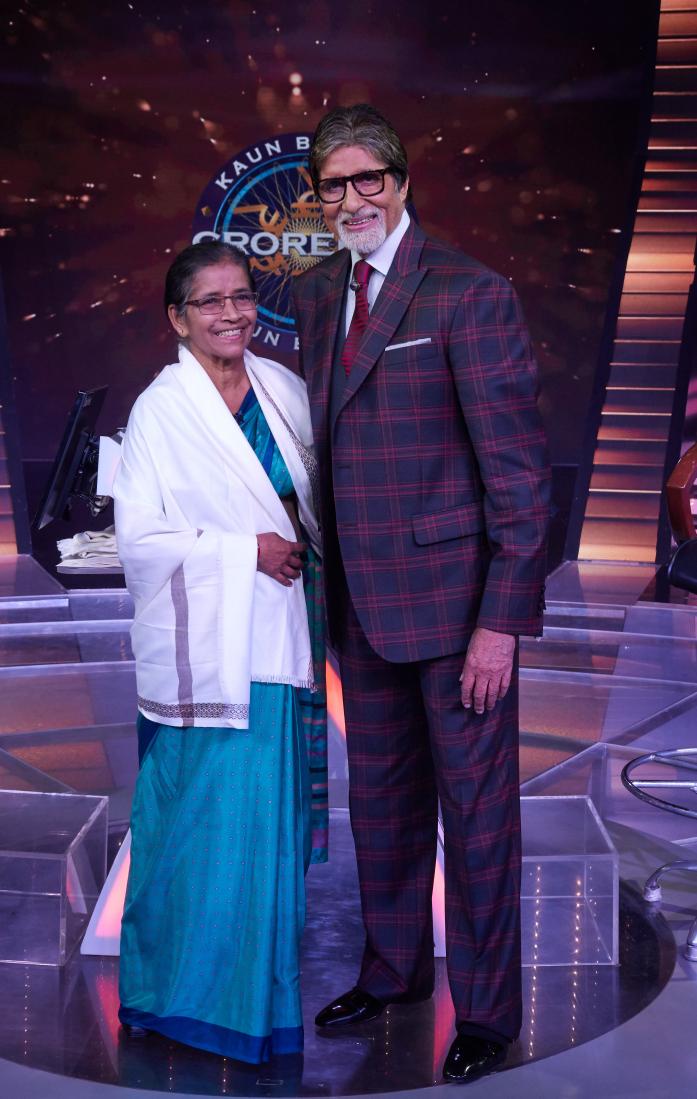

Sudha with Amitabh Bachchan on the show Kaun Banega Crorepati
“While the girls are being educated, many still treat them poorly. I want to change their mindset. Many live in poverty and are marginalised. We are working on several projects to uplift the Musahar community,” she smiles, carrying on her good work.




