(July 10, 2022) “Sid’s Farm has given me everything that I have ever wanted.” Kishore Indukuri, the founder of what is one of Telangana’s most successful dairy farms, speaks straight from the heart. “It wasn’t a typical business, but it pushed me to my limits. It showed me what I was capable of enduring to survive. That’s what I truly cherish.”
What began as a means to ensure his two-year-old son was drinking fresh and pure milk, a small operation that started with 20 cows on a piece of leased land in Shamshabad, is a leading dairy brand today, with an annual turnover of Rs 65 crore. Named Sid’s Farm, after Kishore’s son, Siddharth, the company distributes over 25,000 litres of milk a day. Fresh, raw milk is procured each day from local farmers and put through a series of stringent tests, “an average of 6,500 daily,” Kishore says, during an interview with Global Indian. “The emphasis is on purity – no antibiotics, no hormones, and no preservatives.”
From Massachusetts to Telangana, polymers to pasteurisation

Kishore Indukuri
Always a bright student, Kishore chose the conventional, much-revered Indian Institute of Technology route to building a career. After he graduated from IIT-Kharagpur, he took the full scholarship he was offered at the University of Massachusetts, Amherst, and moved to the United States for a master’s and Ph.D. “Everything was paid for and I enjoyed my research,” Kishore recalls. “But all the while, I felt something was missing in my life.”
Kishore stayed in the US to work at Intel for the next seven years. “It was an amazing time, I got to travel to countries like Japan, South Korea, and Canada. Still, I needed to do something more. I knew that. I just didn’t know what it would be.” One day, he knew he had to take the leap. He walked up to his boss and announced that he was moving back to India with his wife and their infant son. “We sold the house, packed up, and moved back.”
Got Milk?
Back in India, he tried his hand at several business ideas, including providing coaching for competitive exams like the GRE. And every day, he wondered if the milk his son was drinking was safe and pure. The answer wasn’t clear. The Food and Safety Standards Authority of India has strict guidelines on dairy and its affiliate products, but “how far are these implemented?” Kishore asks.

Kishore Indukuri
“India has done so much good work. You can walk to any shop and get a packet of milk,” he adds. “We are the largest producers of milk and we consume all of it.” In this pursuit of plenty, however, the emphasis on quality took a backseat.
As he did his research, Kishore found that India’s dairy industry continues to thrive, recording an annual growth of 12 percent CAGR. Having grown up in an agrarian household, he felt a natural affinity for the industry. “I also learned that dairy had lots of potential as a business venture,” he recalls.
The trial-and-error business model
With two degrees in industrial chemistry and polymer science and engineering, as well as a doctoral thesis on the “squalid mechanics of polymeric materials,” Kishore entered the dairy business as a rookie. So he did what he knew best – hit the books. A veterinarian friend, Ravi, helped him choose his first batch of cows. “He told me, ‘you have to look at the cow’s beauty’. I had no idea what that meant,” Kishore laughs.
He and his wife visited numerous farms across India, learning everything they could. They hired staff to milk the cows and started in the wholesale market. The plan didn’t work. “We were selling at Rs 15 per litre when the cost of production was anywhere between Rs 25 and Rs 30,” he says. So, they decided to sell directly to customers. It meant visiting them personally, distributing pamphlets that his wife designed, explaining the benefits of milk that contains no preservatives, antibiotics, hormones, or thickening agents.
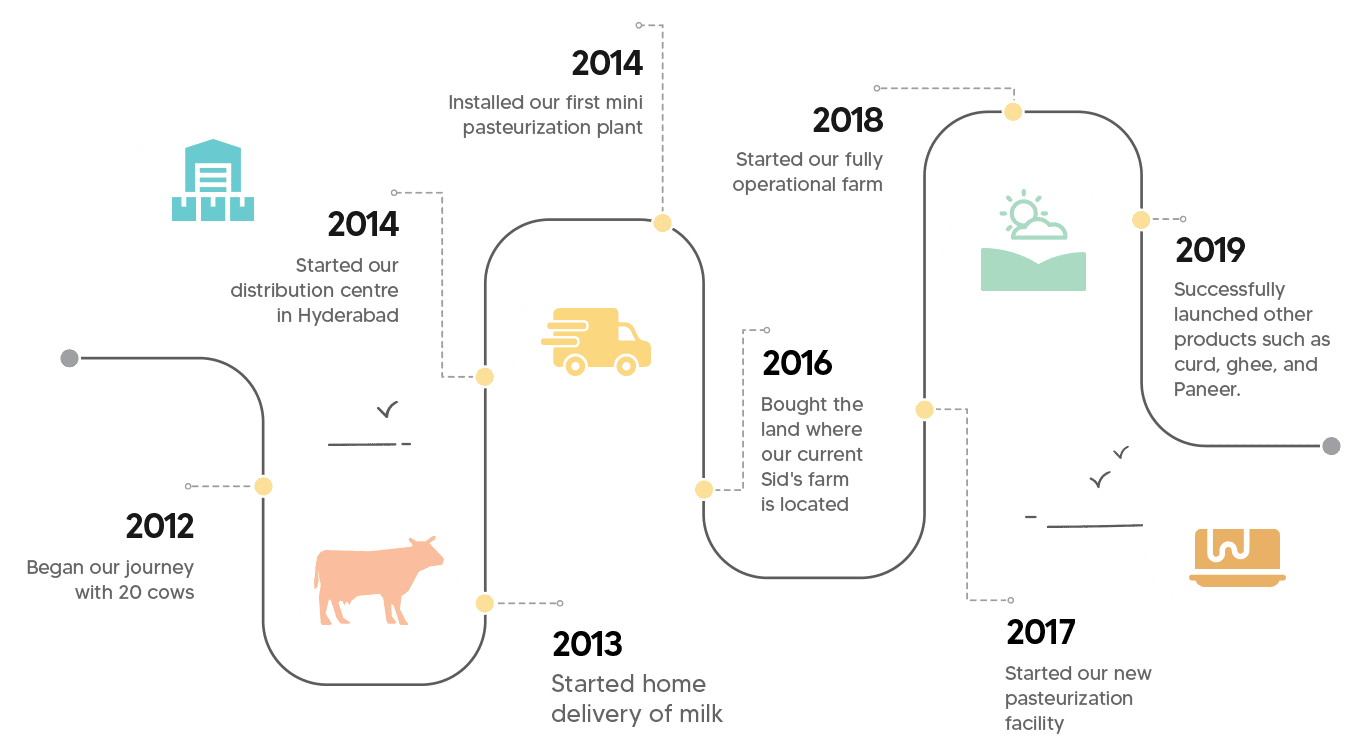
Graphic courtesy: Sid’s Farm
“Milk doesn’t take a break,” Kishore says. “We were transporting fresh milk twice a day, 730 times a year, starting 2013.” The obstacles were many, especially on the distribution side. There were accidents and numerous untold delays. “It doesn’t matter how good the milk is, if the customer didn’t get it in time for his morning coffee, he will go elsewhere.” Eight years later, they do 16,000 deliveries a day and have separate apps for customer interaction as well as delivery. “We didn’t even stop during COVID,” he says.
He recalls another occasion when the staff, who would milk the cows threatened to go on strike, demanding more money. The team was at a loss, the cows needed to be milked. Local farmers took pity on their plight, milked their cows, and then came to help them. “That’s how we started working with farmers, we sell their milk for them.”
Put to the test
Fresh, raw Indian milk is among the best in the world, Kishore remarks, sourced from smaller farmers who keep grass-fed, free-range cows. However, with little implementation of the regulations, thickeners, preservatives, hormones, and antibiotics are a common presence. Making sure their dairy farm produces pure and unadulterated is a point of pride for Kishore, who has never held back from spending on the best equipment. “A lot of the technology is available in India because of our thriving dairy industry,” he says.
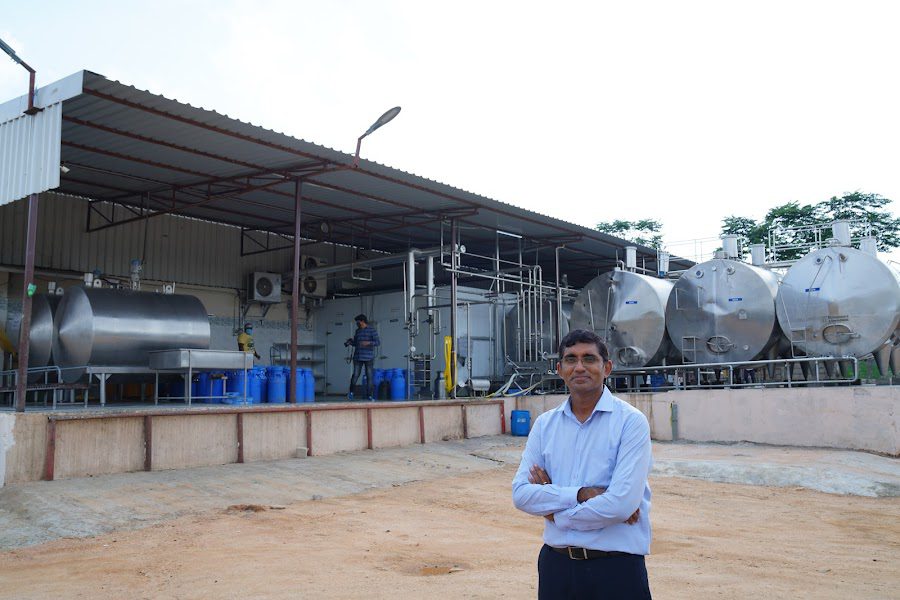

First, raw milk is tested for thickeners, using an ultrasound pulse. Salts, sugar, urea, and maida are commonly used thickening agents, to help the sellers get more value for money. Hormones are also commonly found and used to increase milk production. “When antibiotics are given to a cow, they go from the bloodstream to the milk,” he says. Consuming trace amounts of antibiotics causes microbial drug resistance within the human body – when the medicines are needed, they will not work.
“Preservatives are commonly added too. Nature designed milk to be drunk immediately, but we don’t do that. Bacteria feed on the milk and convert the lactose into lactic acid. The thinking seems to be, if you add a base like hydrogen peroxide or caustic (to neutralise the acid), or modify the pH levels, it won’t go bad.” The answer to this is effective chilling systems – and Kishore insists on the best. “Antibiotic testing alone costs us up to Rs 4 lakhs a month,” he says.
The journey so far
The dairy farm has grown tremendously over the last decade, branching out over the years into other dairy products like paneer, ghee, (made with lemon juice, not synthetic chemicals), curd, and butter, all made in-house. Cow milk and buffalo milk are processed and sold separately. Kishore also hopes to expand to other states soon.
As our conversation draws to a close, Kishore smiles, adding, “There’s one more thing. When we bought this land, there was nothing on it. We have planted over 500 trees in 10 years. We also harvest rainwater to recharge the groundwater table.”


