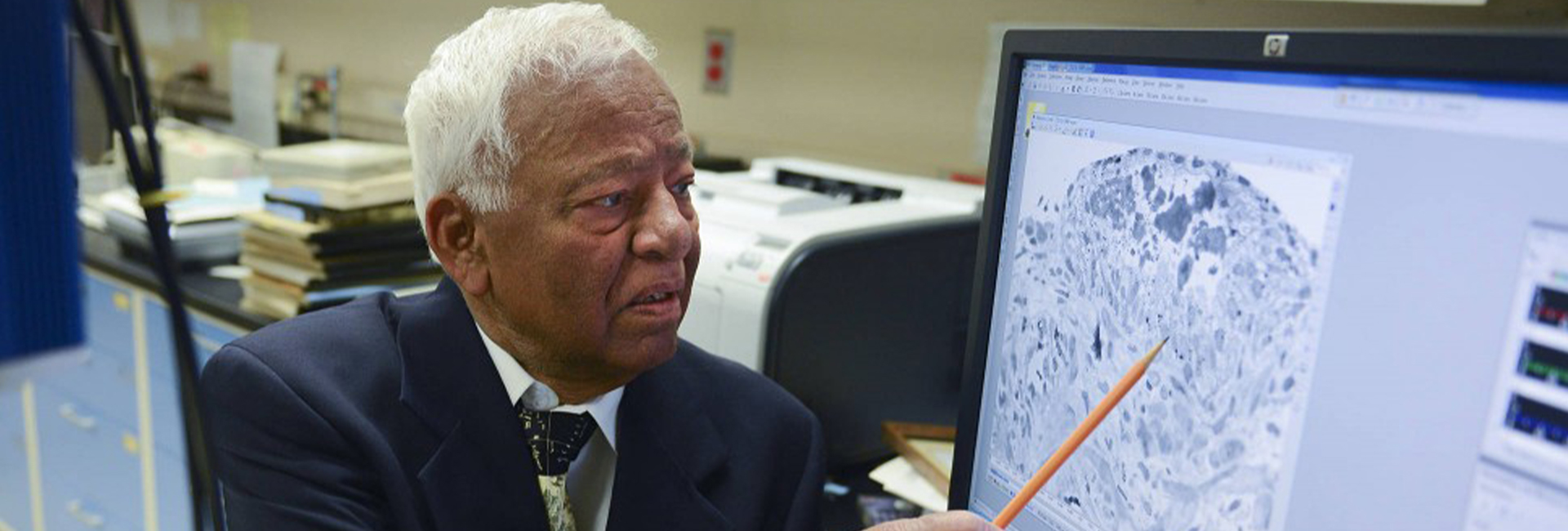
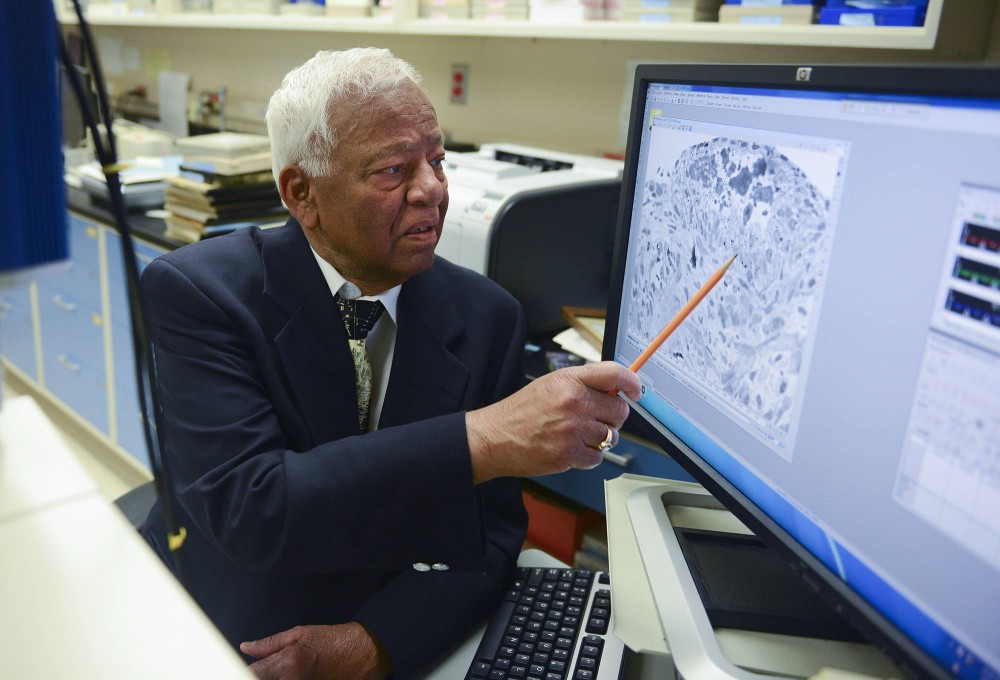
(August 22, 2024) In 2013, Professor Akhouri Achyutanand Sinha, was searching online for information to write a tribute to a former team member, who had passed away. The late team member had accompanied Professor Sinha on an Antarctic expedition in the 1970s. The professor had been on a scientific expedition focused on researching and documenting the populations of seals, whales, and birds that inhabit the pack ice – a floating layer of sea ice – within the Bellingshausen and Amundsen seas of Antarctica. That research had helped establish critical baseline data for future research, climate change debates and United Nations population conservation efforts of wildlife. 40 years later, to Professor Sinha’s surprise, he discovered a Wikipedia entry, revealing that a 990 metres high mountain, located at the southeast end of Erickson Bluffs in the southern region of McDonald Heights in Antarctica, was officially named ‘Mount Sinha’ in recognition of his contributions in the Antarctic expedition.
“Named by US-ACAN for A.A. Sinha, member of the biological party that made population studies of seals, whales and birds in the pack ice of the Bellingshausen and Amundsen Seas using USCGC Southwind and its two helicopters, 1971-72,” the entry reads.
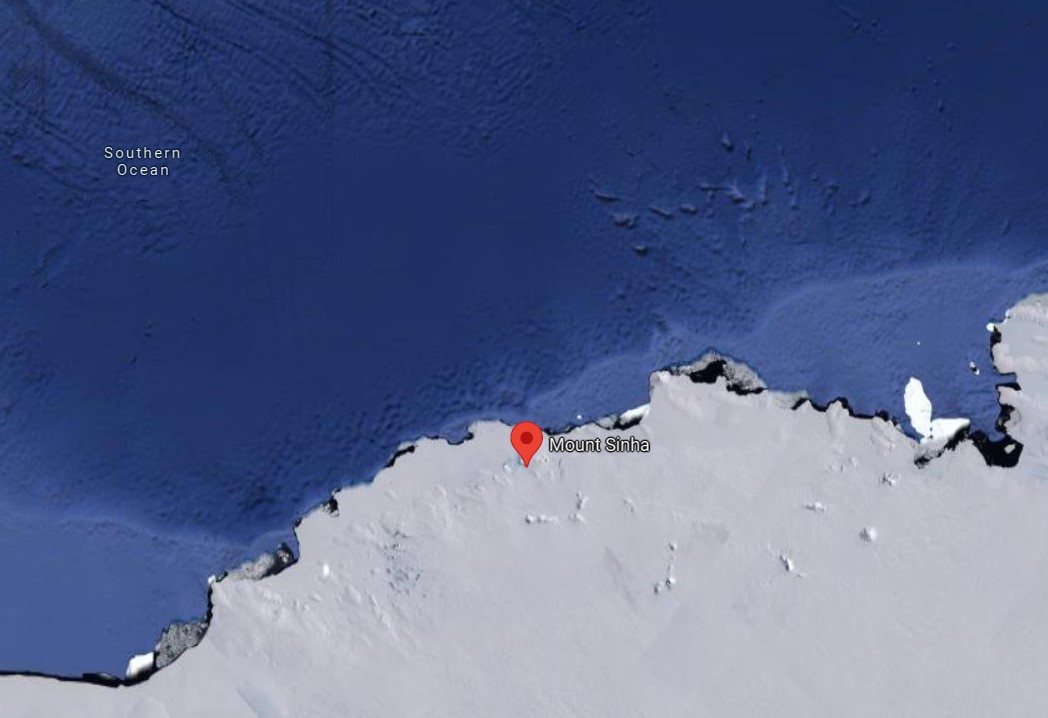
Image extracted from Google Maps
Memorable experiences
Following this discovery Professor Sinha shared with the press, “I went to Antarctica on two expeditions lasting for about 22 weeks on the US Coast Guard cutters, Southwind and Glacier, during 1972 and 1974. We were often dropped via helicopter atop vast sheets of pack ice to research and capture resident fauna, and I was even attacked once by predatory Skua birds near Palmer Station.”
Given his background and expertise in reproductive biology, the US National Science Foundation had invited Dr Sinha to conduct research on the reproduction of Antarctic seals, as part of their Antarctic Program. His work encompassed cataloguing of native seal, whale, and bird species along nearly 100,000 nautical square miles of the Antarctic coast.
Carrying out the studies in the remote and challenging environments, the scientist was mesmerised by the pristine beauty of the place and the superb adaptability skills of the Antarctic animals to the harsh weather conditions.
Along with his team he had even visited countries like Argentina and New Zealand on their way to Antarctica. Between expeditions, Sinha and his crew members aboard their U.S. Coast Guard ship would play poker, rummy and eventually bridge.
Raising alarms on climate change
In addition to his work with animals, Sinha has been one of the key people to first raise the alarm on Antarctica’s depleting ice shelf. According to the University of Minnesota, “Records of population sizes, types and behaviours created by Sinha and his teammates have established critical baseline data that remain relevant in today’s climate change debates.”

Professor Akhouri Achyutanand Sinha
Research conducted by Professor Sinha helped in establishing the continent as an international scientific preserve to protect it from drilling and exploitation for oil, minerals, and other valuable natural resources. The scientist’s research was also used for the United Nation’s early conservation policies to preserve native wildlife of Antarctica.
Professor Sinha had highlighted that since Antarctica is rich in resources such as animal populations, gas, oil, minerals, and freshwater, India and the United States could form a strong research collaboration to tap into these valuable assets and advance scientific understanding to protect the continent’s resources. “India can play a constructive role with a tie-up with the US and can protect habitats and mineral resources of Antarctica,” he had remarked during a seminar in India.
Since the Global Indian scientist’s pioneering biological research expedition provided critical data and insights, the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names (US-ACAN) and the US Geological Survey had named an Antarctic mountain after him within a few years of the expedition – a tribute he discovered decades later.
From Buxar to Minnesota
Sinha who served as an adjunct professor in the Department of Genetics, Cell Biology, and Development, and a professor in the Department of Urology at the University of Minnesota – had moved to the United States in 1961 as a PhD scholar.

Professor Akhouri Achyutanand Sinha
Born in the village of Churamanpur in Buxar district, a village established in 1739 by his ancestor Akhoury Churaman Singha (later Sinha), the research enthusiast earned a BSc degree from Allahabad University and an MSc in Zoology from Patna University. Before moving to the US for his PhD at the University of Missouri at Columbia, he taught in the Department of Zoology at Ranchi College.
After completing his PhD, he took up postdoctoral work, and his first teaching role as an assistant professor at the University of Wisconsin before being accepted to teach at the University of Minnesota in 1981. Professor Sinha taught graduate level courses for more than two-and-half decades.
“In spite of my stay in the US, I have preserved my perspectives in life,” Sinha had shared during one of the felicitation ceremonies of his alma mater, Patna University adding “Earning money is not enough. I know many Indians brag how rich they are. You cannot take money with you, but a good deed will last forever.”
Pioneering work in cancer research
Professor Sinha, who has authored hundreds of research papers, conducted critical studies on the characteristics of prostate cancer stem cells, the aggressiveness of prostate cancer, and cell proliferation and death. He was affiliated with the University of Minnesota’s Masonic Cancer Centre, a comprehensive cancer centre recognised by the National Cancer Institute.
Some of his research works were efforts which were not even funded by grants. He had hired student researchers, paying them out of his own pocket to assist him in his work. “I will do what is right – if you don’t give me money, that’s OK,” the scientist with deep dedication towards his work and life’s purpose had remarked.
Apart from his responsibilities as a professor and cancer research scientist, he held a long-term association as a researcher at the VA Medical Center in Minneapolis dedicated to the needs of veterans, their families and caregivers. “After I moved to VA, I was nudged to work on something relevant to veterans’ diseases,” he had remarked.

Professor Akhouri Achyutanand Sinha
Matters of the heart
Despite being deeply engaged in his work in the US, Professor Akhouri Achyutanand Sinha had not lost touch with his village in Bihar’s Buxar, visiting almost every year to escape the Minnesota winters. The scientist with a fascination for cross-country skiing, travelling, reading, and photography, had met his wife Dorothy K. Pamer at a party in Dinkytown. “He just loves what he does and he says he’s never going to retire,” Dorothy had remarked in an interview.
Encouraging the students in Patna, the alumni of Patna University’s 1956 batch had said during a felicitation ceremony, “Show the world what you are capable of and do not be afraid to talk to people about your research work, and take help from experts.”
Read a similar story of Dr. Manu Prakash, vision for frugal science.




