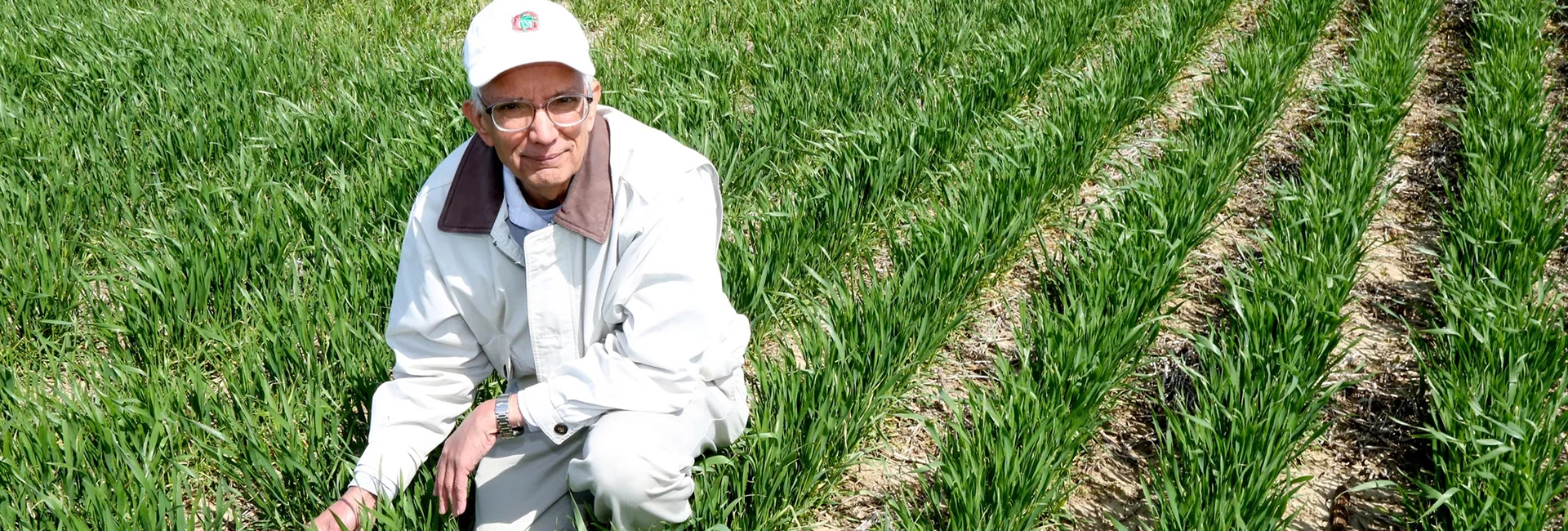
(October 22, 2024) From the sun-drenched fields of pre-partition Punjab to the prestigious halls of academia in the United States, Rattan Lal’s journey depicts how Indian experiences can transform global challenges. Once a child farmer toiling on his family’s modest land, he has risen to become a leading figure in improving food security for over two billion people.
Recently honoured with the 2024 Gulbenkian Prize for Humanity, Lal’s groundbreaking research in soil science is reshaping the understanding of sustainable agriculture and its vital role in addressing pressing global issues, inspiring hope and possibility. With a career spanning more than five decades, his accolades include the Nobel Peace Prize, the World Food Prize, and the Padma Shri, among others. In 2014, he was recognized in the Thomson Reuters list of the World’s Most Influential Scientific Minds. In 2022, U.S. President Joe Biden appointed this Global Indian to the Board for International Food and Agricultural Development (BIFAD), making him a key advisor on global agricultural policy.

Dr Rattan Lal
In a world where the stakes have never been higher, Lal serves as a guiding light, advocating for the respect and dignity of agriculture to attract the next generation. “The agriculture profession must be given the respect and dignity it deserves,” he emphasized in an interview, highlighting his commitment to a holistic vision of agricultural innovation that encompasses business, academia, and industry globally.
From refugee to renowned scientist
Born in 1944 in British India’s Punjab region, Lal’s early life was shaped by hardship and displacement. His family, subsistence farmers, lost their land during the partition and lived in refugee camps for two years. Eventually resettling in India, the Lal family farmed less than two acres of semi-arid land, facing the daily struggles of smallholder farmers—droughts, poor soil quality, pest infestations, and a lack of modern agricultural tools. It was here, as a child farming on the family land, that Lal first became aware of the fragile relationship between soil and sustenance.
These early experiences sowed the seeds of his lifelong passion for soil management, driving him to explore ways to improve soil productivity, particularly for smallholder farmers like his own family.
“My interest in soil and its management goes back to my childhood, growing up on a family farm in north-western India. During those times without fertilizers, tractors, or electric pumps, the wellbeing of families depended on soil and its ability to produce crops.” – Rattan Lal
Education in India and abroad

Dr Rattan Lal during his days as a student
Lal earned his B.Sc. degree from Punjab Agricultural University and his M.Sc. from the Indian Agricultural Research Institute. A significant moment came in the 1960s when an Ohio State University professor noticed his talent and arranged a scholarship for him to pursue a Ph.D. in soil science, which he completed in 1968. This marked the beginning of an illustrious career that would span over half a century, leaving an indelible mark on global agriculture and environmental science.
Early Career – In Nigeria
One of Lal’s most formative experiences came during his time as a soil physicist at the International Institute of Tropical Agriculture (IITA) in Nigeria. It was there, while studying the effects of deforestation on soil health, that Lal made a groundbreaking discovery: removing trees and vegetation caused the organic carbon and essential nutrients in the soil to disappear, rendering the land barren. In response, Lal developed practices such as mulching, no-till farming, and cover cropping to restore lost nutrients and organic matter, effectively regenerating the soil’s fertility.
His findings not only revolutionized local agricultural practices but also attracted global attention. Scientists from around the world travelled to Nigeria to see his experimental plots, marveling at how Lal had managed to bring degraded soils back to life. This research laid the foundation for his future work on carbon sequestration, showing how soil could serve as a natural sink for atmospheric carbon dioxide, thus playing a crucial role in mitigating climate change.
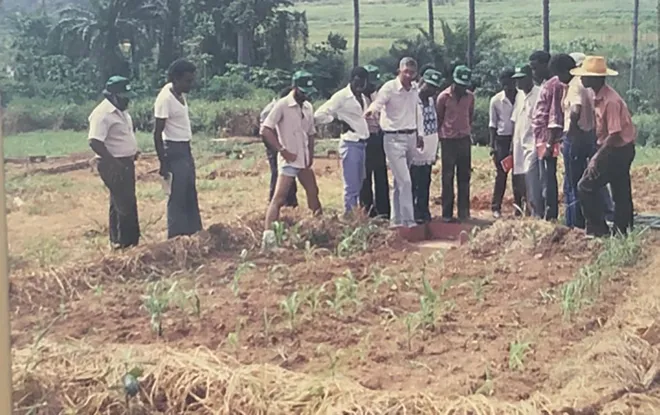

Dr Rattan Lal with farmers at a research site in Nigeria
Returning to Ohio: Leading the world
In 1987, Lal returned to Ohio State University, where he established the Rattan Lal Center for Carbon Management and Sequestration. Over the next several decades, his research focused on transforming degraded soils into healthy, productive ones—not just for agricultural benefit but for the greater ecological good. His models demonstrated that by restoring soil health, humanity could double global annual grain yields, reduce the land area used for grain cultivation by 30 percent, and significantly lower the need for chemical fertilizers, which contribute to environmental degradation.
In 2004, the scientist published a landmark paper in Science titled “Soil Carbon Sequestration Impacts on Global Climate Change and Food Security.” In this paper, Lal was one of the first to assert that restoring organic material to the soil could help remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. “Soil can be a powerful tool in mitigating climate change,” Lal argued. This idea has since become a cornerstone of climate change mitigation strategies and remains one of the most cited works in environmental science.
He continues to be ranked as a highly influential researcher, with over 1,000 peer-reviewed journal articles and more than 100 books (written and edited) to his name.

Dr Rattan Lal is considered the godfather of soil science
Work that aligns with the UN’s 2030 Sustainable Development Goals
Lal’s five decades of work are deeply aligned with the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), established in 2012, particularly those focused on eradicating hunger, combating climate change, and ensuring sustainable ecosystems.
He pointed out that one oversight of the Sustainable Development Goals is that the word “soil” is not specifically mentioned in the primary language of any of the 17 Goals, although the word “land” is included in SDG15.
“It is now widely realized that protecting, managing and restoring “Soil Health” is essential to achieving several SDGs (such as #1;2;13;15 and others). The focus on improving soil health can still accomplish several SDGs in the remaining years.” – Rattan Lal
His pioneering research in regenerative agriculture and soil carbon sequestration directly addresses SDG 1: No Poverty by improving the livelihoods of smallholder farmers, as well as SDG 2: Zero Hunger, significantly enhancing global food security through sustainable farming practices. By focusing on restoring soil health to mitigate climate change, his efforts resonate with SDG 13: Climate Action. Moreover, his advocacy for ecosystem preservation supports SDG 15: Life on Land. As Lal aptly puts it, “Good diet is also good medicine,” highlighting the critical importance of nutrition-sensitive agriculture in achieving these global goals.

Dr Rattan Lal at field work in Ohio
Giving back to farmers and the earth
Despite his academic achievements, Lal has never forgotten the struggles of smallholder farmers like his own family. His life’s work has been about giving back—both to the earth and the people who depend on it. His techniques for restoring soil health are now used across continents, from Africa to Asia to the Americas. More than two billion people have benefited from improved food security due to his soil-centric agricultural methods.
“Keeping food prices low is important but it should not come at the cost of farmers’ livelihoods or the degradation of our planet’s soils.” – Rattan Lal
As a prominent advocate for sustainable agriculture, he has worked tirelessly to ensure that his findings translate into actionable policies. In 2021, he and his team launched the C-FARM project on carbon farming, aimed at providing field-based validation of how soil can capture and store carbon dioxide.
Through his leadership, initiatives like Living Soils in the Americas have emerged, creating international collaborations aimed at preserving and enhancing soil health.

A lifelong mission
At 79, Dr Rattan Lal continues to advocate for policies that support sustainable agriculture, serving as Chair in Soil Science and a Goodwill Ambassador for the Inter-American Institute for Cooperation on Agriculture. Though his many accolades, including the 2024 Gulbenkian Prize, recognize his contribution to protecting the planet’s future, Lal believes the work is far from over. His vision for the future involves continued global cooperation to further soil management, ensuring that future generations inherit a planet capable of feeding its people while thriving ecologically.
Dr Lal not only bridges the gap between traditional farming practices and modern science but also serves as an inspiration for the diaspora to leverage their Indian experiences and knowledge for global betterment.
- Follow Dr Rattan Lal on LinkedIn




