From rugged mountains to bustling cities and serene countryside, cyclists have been embarking on daring expeditions, experiencing the world in a unique and exhilarating way. With each turn of the pedal, they weave through diverse landscapes, discovering hidden gems, and immersing themselves in the beauty of nature and culture. This World Bicycle Day, Global Indian brings you the story of Parsi cyclists who were the pioneers in adventure in India.
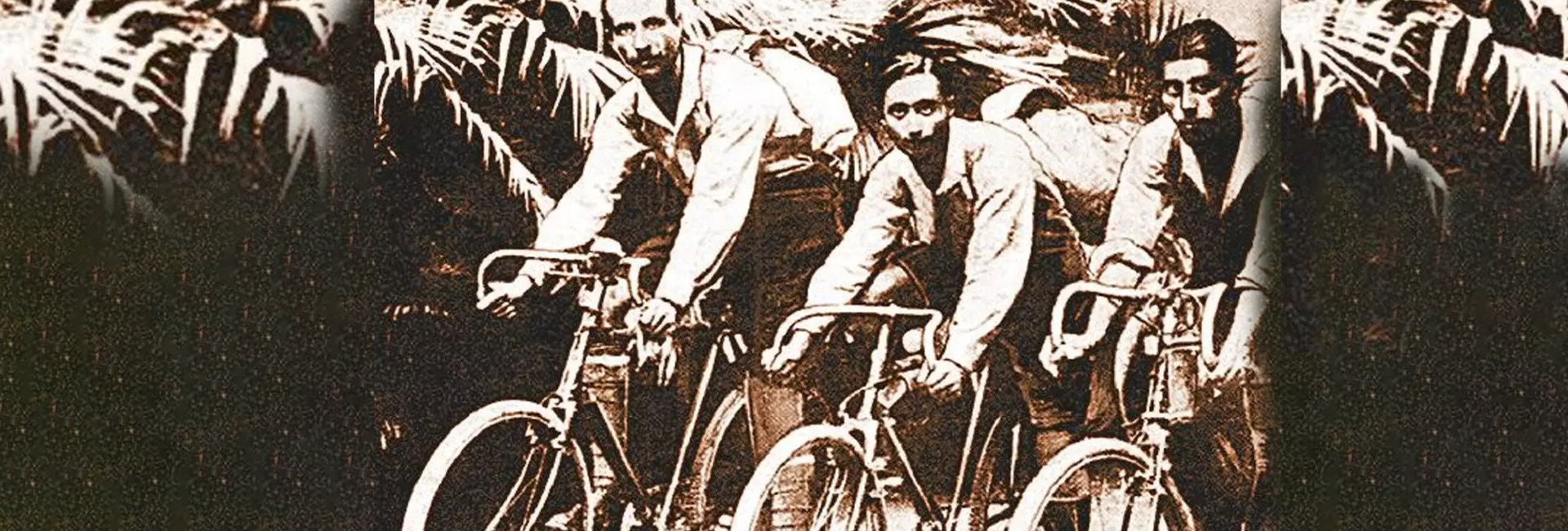
(June 3, 2023) It was a regular Monday for many Bombaywallas on October 15, 1923, but not so for the Bombay Weightlifting Club which organised a send-off for six of its young members — Adi B Hakim, Gustad G Hathiram, Jal P Bapasola, Keki D Pochkhanawala, Nariman B Kapadia and Rustom B Bhumgara – ready for their first cycling expedition across the globe. In two groups of three, these young Parsi lads left to pursue their dream of travelling the world – something that was unheard of in India at that time. It was this novelty which intrigued these Parsi men. Three years before taking the leap of faith, they had huddled together at Bombay’s Oval Maidan in 1920 for a public lecture by a Frenchman who had walked from Europe to India. Inspired by the travels of the Frenchman, they were determined to embark on their extraordinary journey that took them through Punjab, Balochistan, the Middle East, Europe, the United States, Japan, and South East Asia. It wasn’t just the curiosity to explore but the desire to tell the world about India that pushed these men to pedal hard.
In the Bombay of the 1920s, India was reeling under the British Raj and the freedom struggle was slowly gaining momentum in the country. This was the climate in which these seven young Parsi men longed for freedom and adventure – but not without purpose. The daring and intrepid explorers were keen to put India on the global map by pedalling across the world, traversing Amazon rainforests, the Sahara desert and war-torn countries. Driven by their innate curiosity and armed with newly-introduced Kodak film cameras, they embarked on an extraordinary journey. Between 1923 and 1942, they set off on the first-ever expedition by Indian cyclists, putting India on the global map of adventure travellers.

Adi Hakim, Jal Bapasola and Rustom Bhumgara in Ooty.
Scripting history – one pedal at a time
Armed with crude copies of a map, a compass, some layers of clothing, a medicine box, cycle gear, and some money from their savings, these men took off on their adventure on British Royal Benson cycles fitted with Dunlop tyres, however, without letting their families get a whiff of their plans. Fearing opposition, they left quietly. In fact, one family only found out about the world expedition when the men had reached Persia. The journey made these men the first Indian eyewitnesses of strife-torn Africa, the ravages of wars in Europe, and America’s Great Depression.
Those long months on the road in extreme terrains and weather conditions weren’t easy for these men. But they worked together as a team to keep their dream of exploring the world afloat. Bapasola, adept at reading the map, became the team’s GPS on the journey while Bhumgara, an auto mechanic, helped repair cycles throughout the expedition.
Adventure in the unknown
After pedalling for months, of them, Nariman returned to India from Tehran owing to personal reasons, while Gustad decided to stay back in America after being enamoured by the country and its culture. However, the trio of Hakim, Bapasola and Bhumgara continued to pedal 71,000 km over four-and-a-half years across terrains. Some days they went without water and some days without food. Avoiding the sea, they took over some of the most difficult routes that no cyclists had undertaken before. “We wanted to know the world more intimately and to acquaint the world with India and Indians,” they said years later. Their expedition had them cross the snow-covered Prospect Point in Ziarat which is 11,000 feet above sea-level to enter Iran and then move towards Baghdad. But it was the journey from Baghdad to Aleppo in Syria that was one of the most treacherous, as they braved sandstorms, parched throats, and temperatures over 57 degrees Celsius. In return, they set a record by crossing the 956 km Mesopotamian desert in just 23 days.

They later sailed to Italy and rode across Europe to reach Britain, and then left for America in the next three weeks, where they cycled 8,400-km across the East to West Coast over five months. Tired, they took the much-needed break when they boarded the cruise to Japan after months of gruelling. Keeping up with their adventure streak, they became the first bikers to reach the ‘Hermit Kingdom’ of Korea and then moved along China. The last leg of their expedition included cycling through Cambodia, Vietnam, Thailand, and Burma before entering North East India and reaching Mumbai in the March of 1928, where they were received amid applause and garlands.
Their adventures were later inked forever when the trio published With Cyclists Around The World in 1931, which had a foreword by Jawaharlal Nehru. “I envy the young men who have made the book. I too have some of the red blood which seeks adventure; something of the wanderlust that even drives one forward. But fate and circumstances have prevented from satisfying it in the ordinary way – I seek adventure in other ways,” he wrote.
Lost and found
But over the decades, their story was lost, until Anoop Babani, a cyclist and former journalist, came across the book in 2017, and upon research found that there were three groups of Parsi men, who over two decades, travelled across the globe. His wife, writer-painter Savia Viegasa, dug deep into their stories as the duo contacted the families of these unsung heroes, and even curated a photo exhibition on the cyclists in 2019 titled Our Saddles, Our Butts, Their World. She realised that the Parsis were the closest to the British, they often took up many allied activities that the British did in India, including love for exploration and adventure. That’s one of the reasons that they were the first ones to take on the world expedition, followed by the desire to carry the name of Mother India to far-flung areas.
Inspiring a new generation
Babani found that the cycle expedition trio inspired Framroze Davar, a Parsi sports journalist from Bombay, to set off on a solo cycle voyage. It was after nine months on the road that he reached Vienna where he met Gustav Sztavjanik, an Austrian cyclist, who was so impressed by his journey that he decided to join him, and the two explored the world for the next seven years.
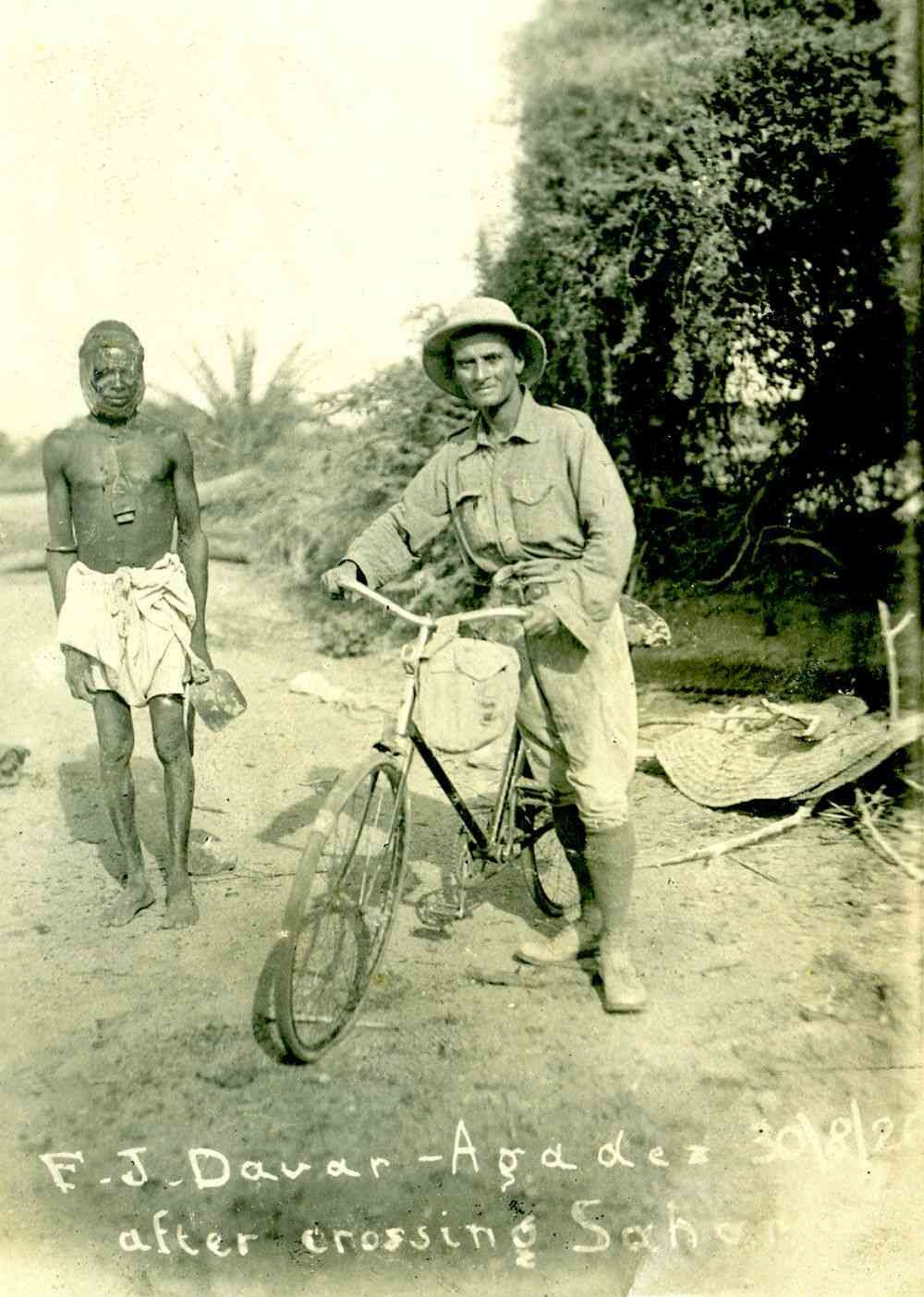

Framroze Davar at Sahara desert
“Theirs was the longest, toughest, and most adventurous journey,” Babani told Scroll. From pedalling in the Sahara desert and Amazon forests to riding over the Alps and parts of the Soviet Union, the duo braved sandstorms, snow, and the worst weather conditions. At times, the terrain was so thorny that they had to stuff grass in the tyres to push them across. En route, they even contracted malaria. However, it was the ride through the thick forest of the Amazon that was the most challenging part of their journey. “It was their first such trip ever from the West coast to the East coast of South America and took them about nine months,” wrote Austrian author Hermann Härtel in a book on Sztavjanik, adding, “This was uncharted territory and very dangerous. Many explorers before them never made it back out again.”
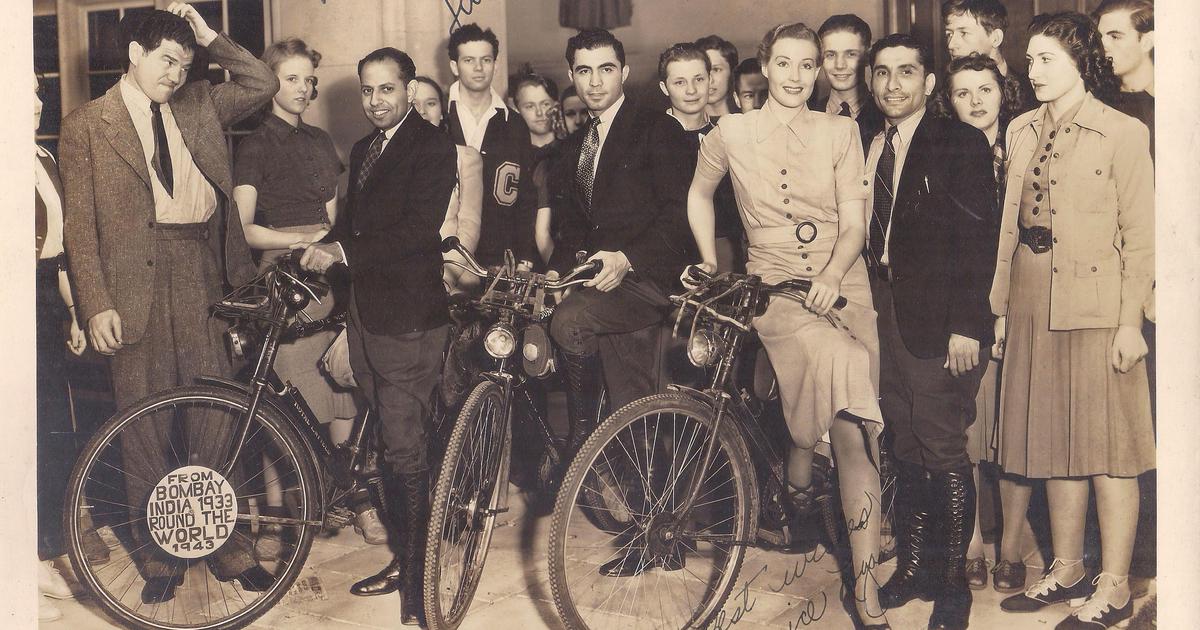
Davar, who covered 52 countries and five continents, ended up penning three books on his travels – Cycling Over Roof Of The World, Across The Sahara and The Amazon in Reality and Romance. According to Scroll, these adventurous stories inspired another group of Parsi men Keki Kharas, Rustam Ghandhi, and Rutton Shroff to cycle the world in 1933. They too covered five continents and 84,000 kilometers, and ended up chronicling their adventures in two books: Pedaling Through The Afghan Wilds and Across The Highways Of The World, where they wrote extensively about being days in a desert in Afghanistan without food and water and were suspected British spies in eastern Turkey.
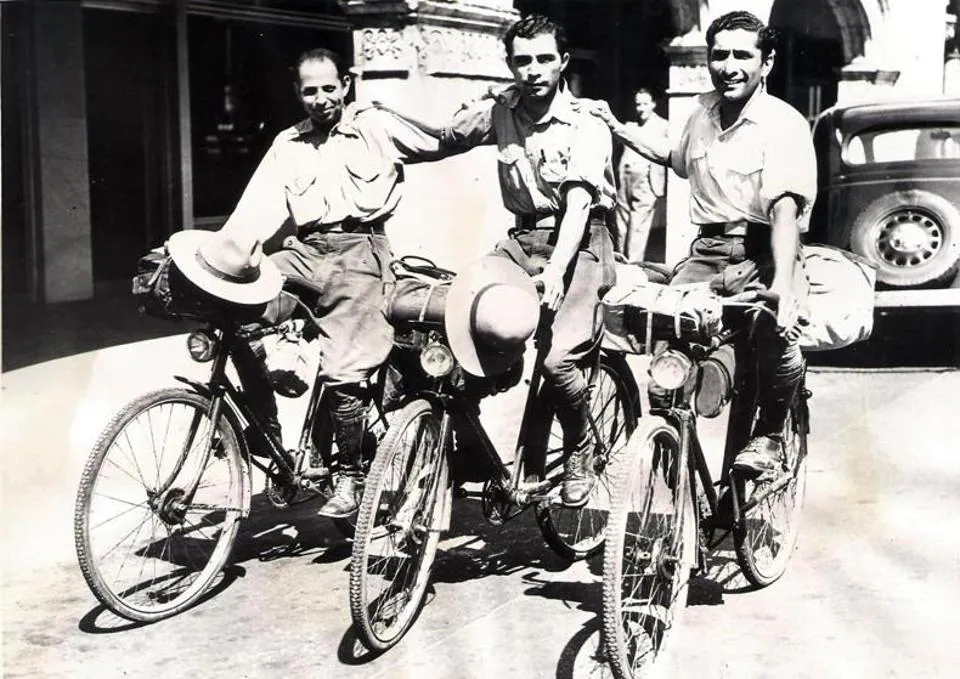

Keki Kharas, Rustam Ghandhi and Rutton Shroff in New York
These Indian cyclists were not just keen to see the world but also acted as nothing short of brand ambassadors of India at a time when not many dared to take the path unknown. “It has a lot of relevance because sports history is going to become a part of academics. [It also serves as inspiration] for younger people. These cyclists went through such hardships; they made themselves into some kind of superhuman machines, travelling with cycles that did not have the wherewithal to go through the desert heat, for example [they stuffed it with straw to make the tyres last].” These Parsis not only put India on the global map but also showcased the power of human curiosity, resilience, and the transformative potential of travel.




