(April 26, 2023) The growing concern around the arsenic contamination of groundwater has become a public health distress in recent years. So much so that the number of people affected by arsenic-contaminated water has meteorically gone up in more than 20 countries, including India and Bangladesh. It was these statistics that made Indian-American teen Ankush Dhawan comb through reams of research to come up with an innovative project – an advance and cost-effective method to test arsenic concentration in water – which made him one of the finalists at the Regeneron Science Talent Search award 2020. Not only has his research earned him a spot among the most promising young scientists in the United States, but it has also opened the door to a brighter future for millions of people at risk from arsenic-contaminated water.

Ankush Dhawan
Ankush’s journey into the world of science began at a young age. Growing up in a family of engineers and doctors, he was surrounded by people who encouraged his curiosity and nurtured his love for learning. As a child, Ankush was fascinated by puzzles and riddles, which later translated into a passion for scientific research.
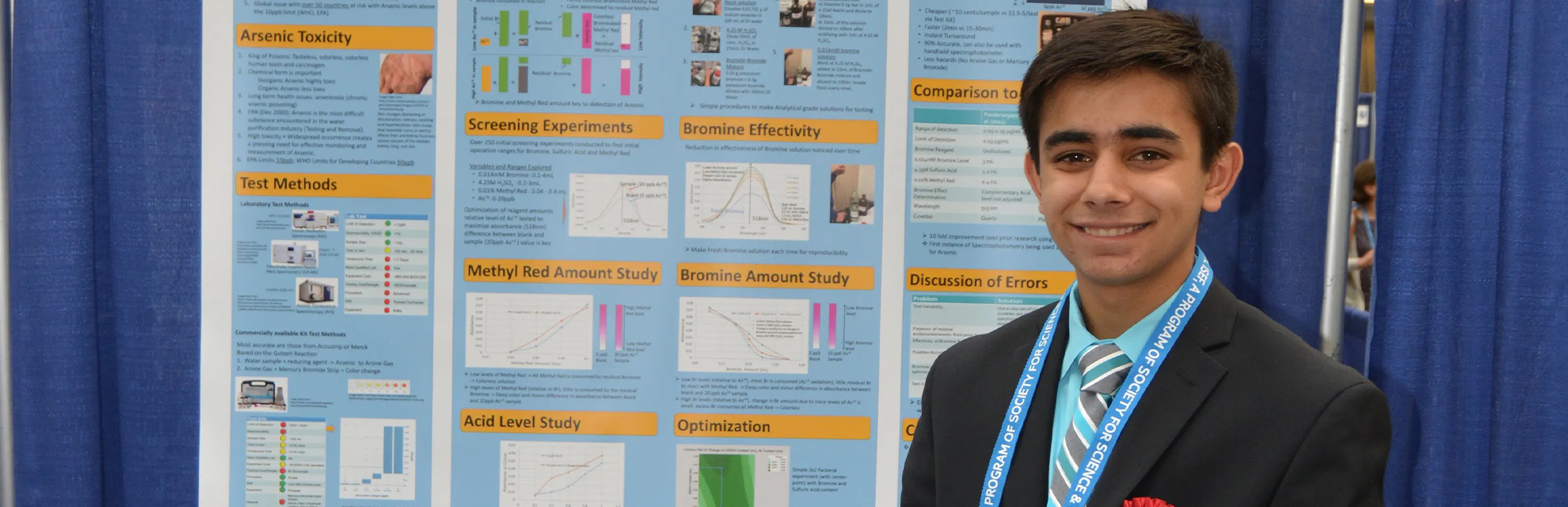
It wasn’t long before Ankush’s interests led him to explore the fields of chemistry and environmental science. When he learned about the devastating impact of arsenic contamination in water supplies, particularly in countries like India and Bangladesh, he felt compelled to address the issue. “Arsenic is a poisonous heavy metal that is found in drinking water all across the world. Over 130 million people have suffered from arsenic-contaminated water. I developed a method to test arsenic and quantify it at trace levels that is an improvement in cost and effectiveness over current tests methods,” the Global Indian said in a statement.
Ankush’s project – An Improved Method for Trace Level Arsenic Quantification in Water – involved developing a method that was more sensitive, accurate, and cost-effective than existing techniques. His approach combined the use of gold nanoparticles with a unique surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) technique.
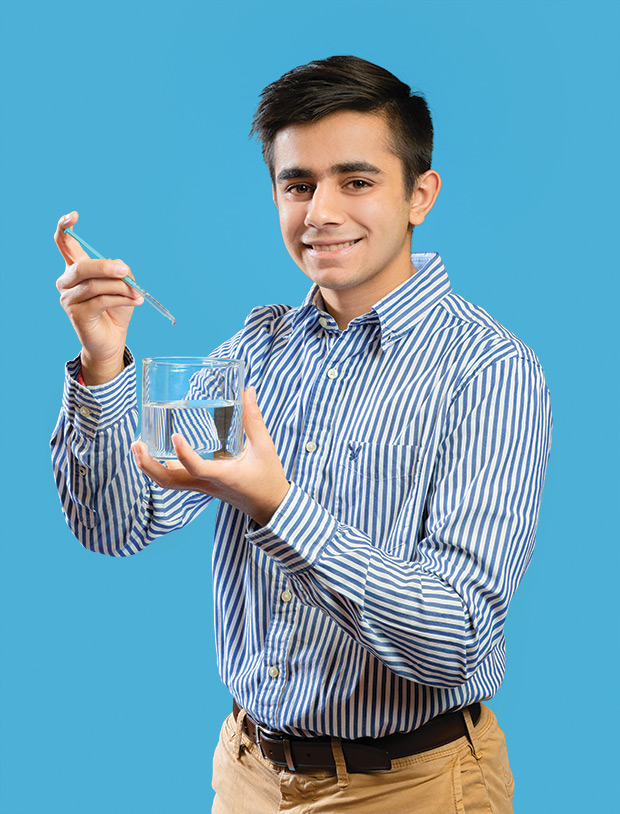


As arsenic is naturally present at hazardous concentrations in much of the world’s groundwater, EPA US, recognising its adverse effects on human health, reduced the arsenic drinking water standard in 2006 from 50 ppb to 10 ppb. However, accurately measuring arsenic below 20 ppb requires water supply companies to use costly analytical techniques. Recognising his work, Regeneron Science Talent Search mentioned that by refining a previously developed method, Ankush was able to reduce the detection limit to 3.5 ppb. Moreover, to detect arsenic in remote areas, he developed a fast and portable visual test that, once commercialised, could be used to detect arsenic concentrations of about 50 ppb for less than one-tenth the cost of existing methods.
His dedication to his research has earned him numerous accolades and awards, including a spot in the top 40 finalists of the Regeneron Science Talent Search 2020 as well as the 2018 Top Young Scientist Award at the Hoosier Science and Engineering Fair.
In addition to his academic accomplishments, Ankush is an active member of his school’s science club and chess clubs and has volunteered for Vanderburgh County’s Teen Court system. Moreover, he has an asteroid in the Milky Way galaxy named after him through the Massachusetts Institute of Technology Lincoln Laboratory. Ankush’s enthusiasm for research and problem-solving has led him to mentor younger students interested in science and to conduct workshops on the importance of clean water and environmental conservation.
Ankush, who is currently an undergraduate student at Stanford University majoring in Electrical Engineering, credits his interest in engineering and the environment to his parents. He believes that science has the power to transform lives and that young scientists can make a meaningful impact on the world.
As a finalist in the Regeneron Science Talent Awards, Ankush has already made a mark on the scientific community. His research has the potential to revolutionise the way arsenic contamination is detected and managed in water supplies across the globe. He wants to economically commercialize his award-winning arsenic test kit once it is patented so that people suffering from arsenic contamination in developing countries can benefit from it. “I would like to potentially commercialize this in the future and get it out to the people who are suffering from arsenic contamination, in areas such as Bangladesh and India. Those are places where contamination is the worst,” he said.
- Follow Ankush Dhawan on LinkedIn