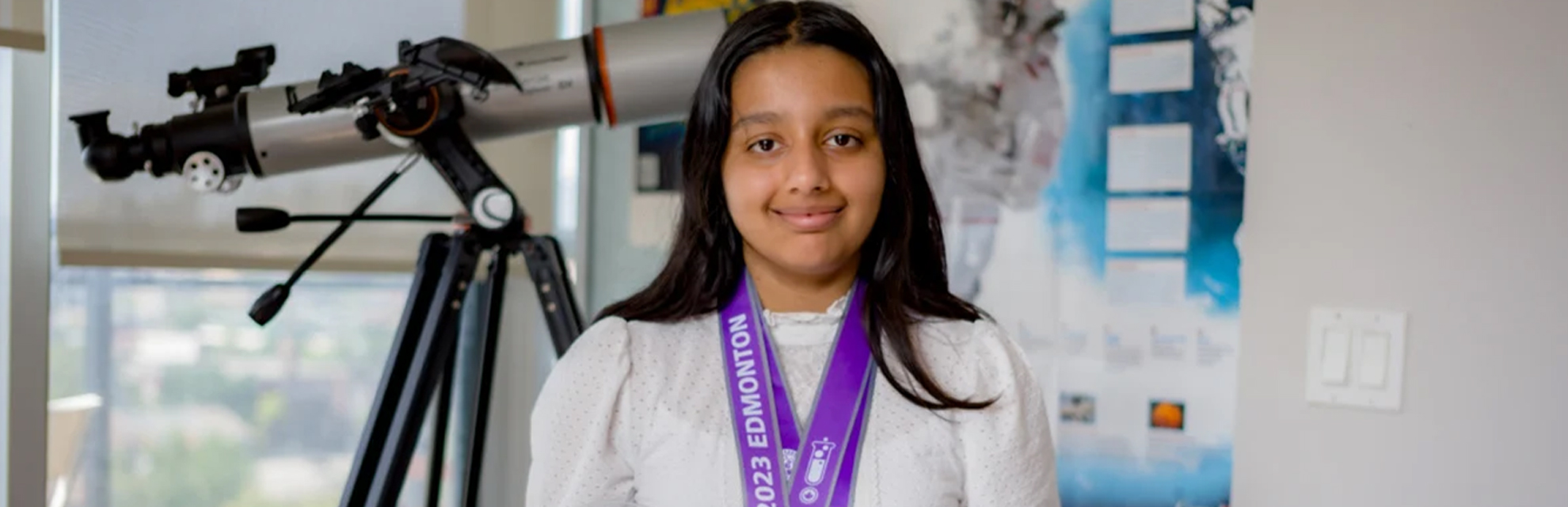
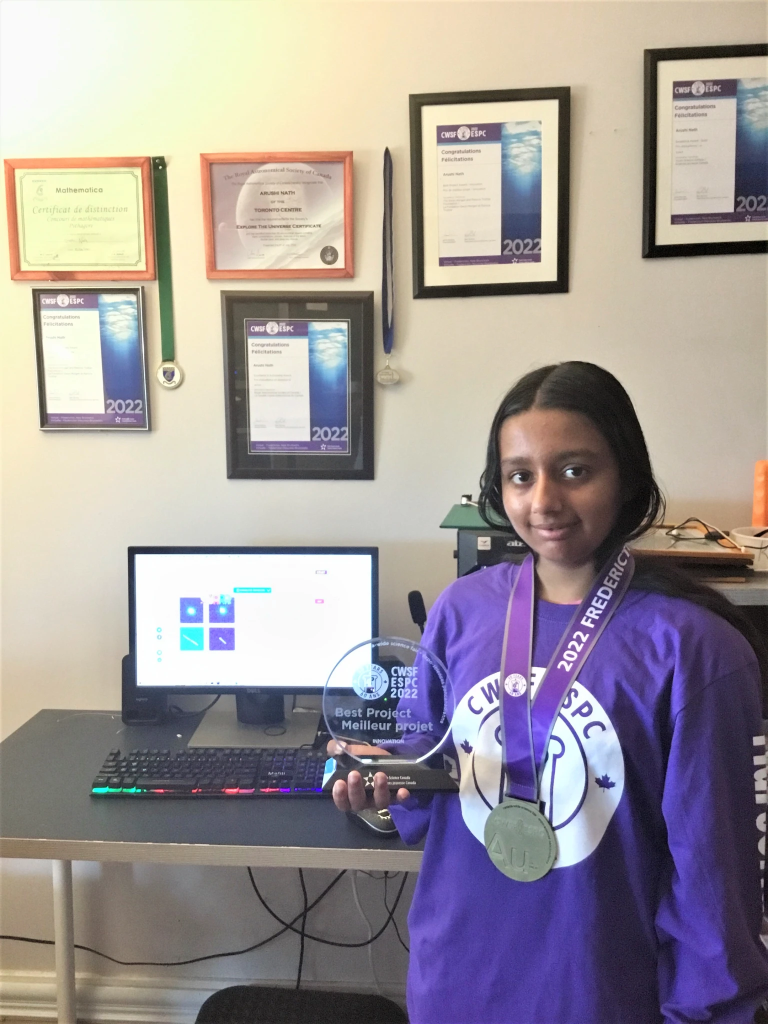
(December 19, 2023) At the 2023 Canada-Wide Science Fair awards gala in Edmonton, nearly 900 attendees celebrated the achievements of Canadian students. Among them, fourteen-year-old Arushi Nath, the founder of MonitorMyPlanet, became the first back-to-back best project award winner since 1989-1990, claiming the prize in 2022 and then again 2023. Her project on planetary defense, focusing on detecting unknown asteroids using open data, mathematics, and Python – her algorithm did actually manage to locate three unknown asteroids. Arushi already has a long list of achievements to her name – she came in second at the European Union Contest for Young Scientists in 2023, the winner of the 2023 Young Astronomer Award from the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada. In 2020, at the age of 11, she won the NASA SpaceAppsGlobal Challenge and in 2017, was the Canada SpaceApps Winner when she was eight years old!
A young genius
Arushi’s scientific journey began young – she has been learning on her own for years. Growing up in Toronto, she would spend her time looking up at the night sky when she was four or five years old. Soon, the family got their first telescope, and Arushi would “observe planets, stars clusters and sketch the observations,” she said. Academically, she had long since surpassed her school work, and wanted to spend her time pursuing her interests. One of these was sparked during her weekly family trips to the Ontario Science Centre, where she learned about the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada (RASC). “They were hosting a monthly meeting inside the Ontario Science Centre, and I was really curious, so I listened to one,” Arushi said. The meetings at RASC, where astronomers and scientists presented their projects, further fueled her interest.

Arushi Nath
As she matured, Arushi’s interests diversified. “I also have other interests, for example, I have been learning to code in Python for the last four or five years. So, I definitely wanted to have lots of coding involved,” she says. She also loves Math, which she learns on her own, saying, “I’m always one or two steps ahead of my school because the subject amazes me so much.” All these interests would eventually come together in the project that helped her win the Canada Wide Science Fair.
The hackathon veteran
As far as Arushi was concerned, doing projects was the best way to learn. She also wanted to bring her scientific acumen together with the things she cared about. So, in 2018, when she and her friends attended the School Strike for Climate started by Swedish Climate activist Greta Thunberg, Arushi wanted to do more “than raise slogans or wait for others to act,” she said. This led to her designing ‘Schools and NASA Aiding Climate Action by Kids’, which comes with the catchy abbreviation, ‘S.N.A.C.K.’. The project uses satellite imagery to calculate tree densities of schools in Toronto, than ranks and maps them. She also designed a pollution sensor to measure levels in parks and schools across the city, using Arduino, the open source electronics platform that lets users create interactive models. “I wanted school children to come up with local solutions to global challenges,” she says.
Her efforts resulted in her being named the NASA SpaceApps Global Nominee – she had already won the Space Apps Challenge in 2014 and again in 2018. In fact, by the age of 10, she had been at a jaw-dropping 29 hackathons. This was a special win, though, she says, of S.N.A.C.K, as it was her first solo attempt. ” I had to do all the work myself, from thinking of the idea, making it, coding and presenting it to the judges in 40 hours.”
The dragonfly drone
As far as Arushi was concerned, doing projects was the best way to learn. During the Covid-19, she began work on her first major endeavour – building a drone – quite a feat for the young scientist, who was only 10 years old at the time. The idea for the directional dragonfly drone was born during the COVID-19 lockdown. Disturbed by the news of locusts devastating crops in Asia and Africa, Arushi saw an opportunity to make a difference. “These locusts often travel in large swarms, are very fast, and can change direction unpredictably,” the Global Indian explained, underlining the urgency of the problem.
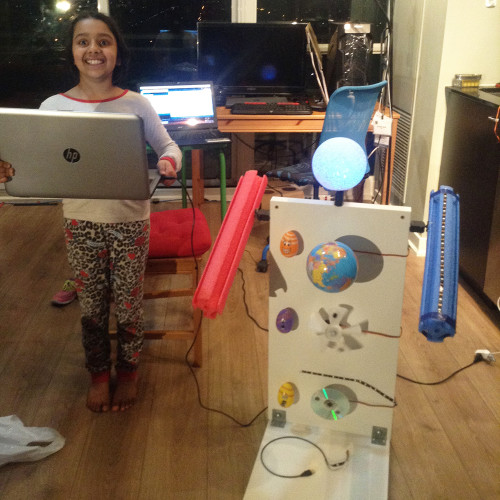


Arushi’s solution was to use drones for locust control. “I thought of using drones, as they can fly, follow the locusts, and monitor their behavior,” she explains. She also wanted to biomimic nature, choosing the dragonfly because it is by far the most efficient hunter, with a 95 percent success rate in catching prey (in comparison, the success rate of lions is 25 percent and sharks have a 50 percent chance of success). Developing a drone is no mean feat, and Arushi used her Lego base to create the foundation and then attached motors and sensors to it, in a meticulous trial and error process. “I programmed it to identify all red objects as locusts,” she said, describing the functionality of her creation.
The planetary defense system
By this time, Arushi Nath was also involved with the Royal Astronomical Society of Canada. She started out attending meetings and listening to others speak but before long, she was presenting her own findings as well. She was also learning how to code in Python, “I started on my own and did many tutorials on Coder Dojo and Kids Code Jeunesse,” she says. And she wanted a way to put all these passions together.
Her idea was planetary defense against unknown asteroids. She had learned about robotic telescopes through the RASC and utilised images from these devices – “I took images from robotic telescopes in Canada, Spain, the US, and Australia to get full sky coverage,” Arushi explains. She had to sift through these to pinpoint the unknown asteroids, using the Gaia Star Catalogue for information on star positions, and the NASA Horizon dataset, for predictions on the locations of known asteroids. Then, using her coding and math skills, she developed an algorithm to filter out known entities – “I created custom masks to remove all these objects, leaving me with the unknown objects,” she explains.
She couldn’t always go it alone, though, often turning to online forums for help. “When I got some errors, I would try for days, even weeks, on my own to find the answer, but if not, I would reach out to specific forums,” she says. She also reached out to experts, including Christina Thomas, the lead investigator on NASA’s DART mission. “”I sent her a message, told her about my current project, and asked if I could have a Zoom meeting to talk to her about her project and how it could relate to mine,” Arushi smiles. Thomas responded and the two did get on that Zoom meeting. “I actually asked her for pointers on my project and what I could do,” she adds.
Finding acclaim


“The whole thing took about ten months to complete,” Arushi says, “From getting the idea, reaching to people to see if they approved of it and then starting to code.” Her goals changed along the way, so much so that her first goal and the end result were very different.” Finally, her findings were sent to the Minor Planet Center database. Then came waiting for a response. “A couple of weeks later, I got an email and three of the asteroids had my name next to them,” Arushi smiles. She submitted her project to the Toronto Science Fair and won gold, qualifying for the prestigious Canada-Wide Science Fair, where she also went on to win. “I was watching the results with my family and wasn’t expecting my name to pop up again but it did,” she says.
Now, Arushi Nath is continuing work on her planetary defense project. Now that the DART Mission has successfully entered the Didymos (asteroid) system, she wants to measure the changes of the system during this impact. “I began studying the Didymos binary system for a copule of months before the DART impact,” she says, “To fully understand how it has been affected.”
Follow Arushi Nath on LinkedIn