During a vacation to Costa Rica in 2018, then ten-year-old Moitri Santra saw that the waters seemed red and brown. Although she didn’t know at the time, she was looking at Red Tide, one of the many harmful algae blooms that release toxins which are fatal to fish, shellfish, marine mammals and birds which feed on the poisoned fish. Apart from this, these harmful algal blooms deplete the oxygen available in the water. Moreover, she noticed signage all over the beach, warning people not to go in the water. The Global Indian would go on to create a solution to harvest harmful algae when it is still alive and potentially turn it into biofuel.
What are Harmful Algal Blooms?

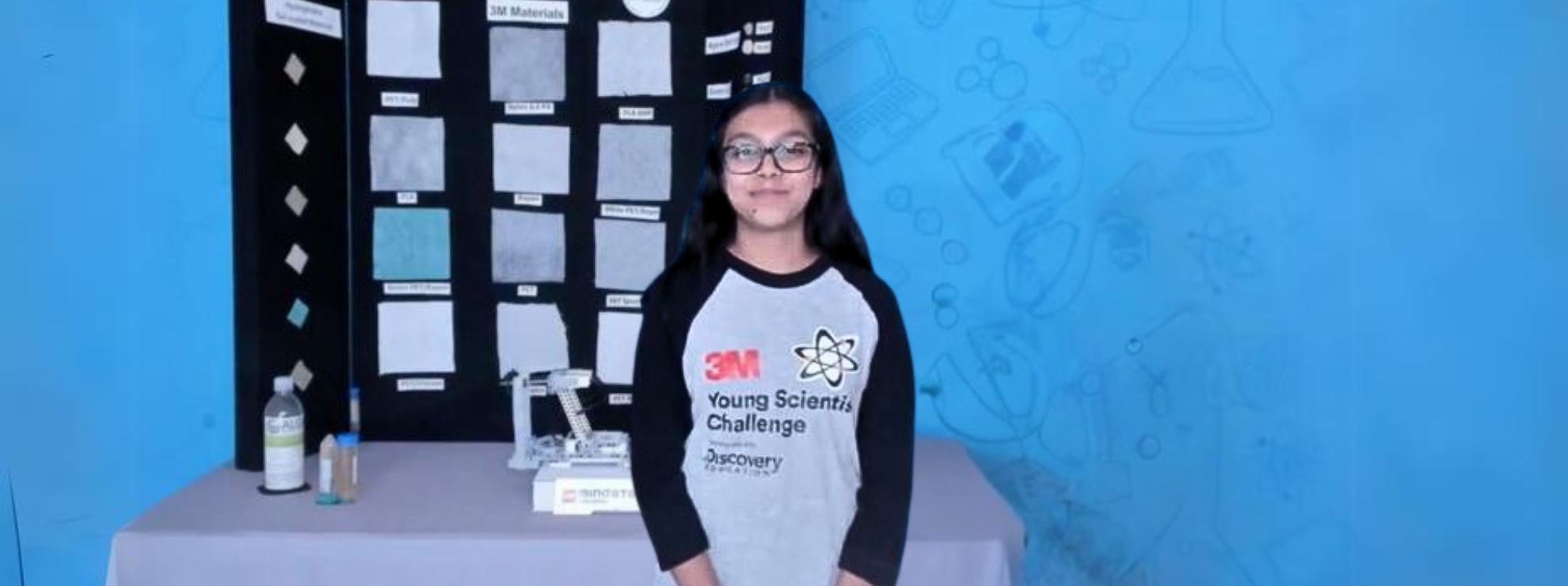
Moitri Santra
When Moitri Santra got home to Florida, she began researching toxic algae, discovering that it is a rapidly growing concern. She found a seven-year study by UNESCO’s Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission, the harmful algae event database had record 9,503 events with impacts on human society. “It contaminates marine life and sea food,” said the teenager, during her presentation for the 3M Young Scientists Challenge. She went on to develop a robot, and a film gel that can attract algae to a substrate. Her vision is to be able to clear the oceans of Harmful Algal Blooms by collecting the algae alive and converting it to biofuel.
Harmful Algal Blooms occur naturally in waterbodies, and can also be encourage dby human activities. Phosphate and nitrate runoffs from fertilizers, as well as from sewage and leachate (liquid from solid waste), along with excessive sunshine can cause harmful algal blooms to proliferate. They also ten dto prefer warmer, still and more shallow waters. Huge amounts of money are spent to clear water bodies of these HABs, the US alone spent $1.1 billion in 2020. Also, there are products to combat these blooms, but Moitri says they just aren’t up to the mark, or are pollutants in themselves.
Moitri’s solution
“I created a water soluble, biodegradable and positively charged gel with a citrate ion and citric acid,” Moitri explains. The chitosan and citric acid contained in the gel induces coagulation in the algae. She spent a summer vacation experimenting with gels and substrates, transforming the family dining room into her makeshift lab. “These algal blooms are everywhere but are especially prominent in Florida,” she explains.
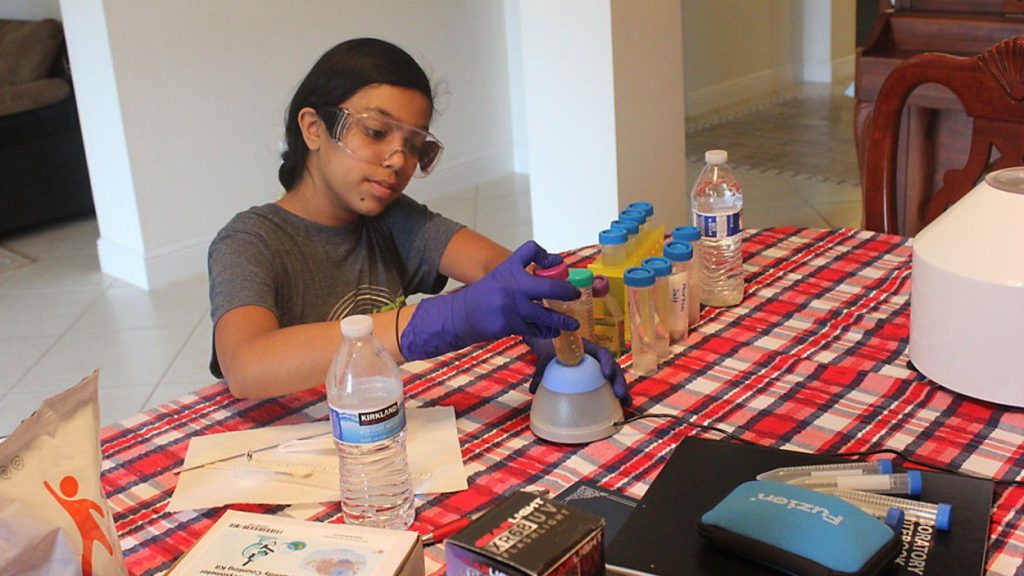


Moitri’s gel is designed to be biodegradable and water soluble, reducing its environmental impact. The chitosan polymer swells and carries the citric acid in water in the gel. The gel induced coagulation in the algae, causing it to clump together, become dense and sink to the bottom. However, the process also causes them to die. However the decomposition process depletes oxygen from the water, killing off marine life all around it.
A functioning prototype
Her 3M mentor, Dr Kannan Seshadri helped her with a turnaround. Moitri Santra realised that algae can be harvested to make biofuel, which comes with environmental benefits of its own. “I experimented with gels, powders and flakes and found that dried film gel floats effectively on water, and attract algae in under a minute. However, this requires a substrate material to trap the algae. In her early version, Moitri had used a scotch brite sponge, which is a non woven material with intertwining fibres. “I experimented with around a dozen non wovens in rayon, viscose, wood pulp, PA and nylon,” she explains. “I chose only the hydrophobic ones because the hydrophilic materials will soak up water and become heavy. Finally, she settled on PET non-woven material.
But after all this, how is the algae harvested? For this, she built SCARAB, an EV3 robot that can be deployed on a boat. The substrate is tied to spools and fastened under a ‘guide’ to hold the material in place. The material is coated with gel and when the motors are turn on, the spool spins slowly counterclockwise, ravelling and unravelling the substrate to collect algae. The material of the substrate also allows the algae to become trapped. “The algae are alive at the end of the process. I examined it under a microscope and it was clearly moving,” she adds.
The 3M Challenge and Broadcom Masters
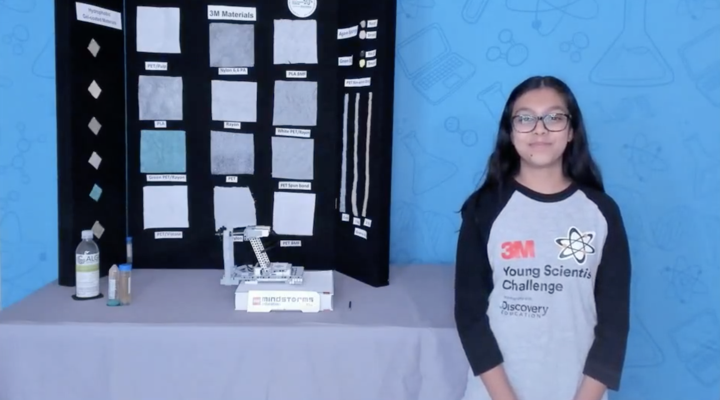


She attributes much of her success to her mentor, Dr Kannan Seshadri. “He helped me turn my simple idea into a functioning prototype,” Moitri says. “I was thinking of sinking the algae and he allowed me to see that it could potentially cause more environmental harm.” Moitri’s next challenge is to remove the algae from the strip without damaging it, which she hopes to do with a primer. “If the right primer is used it can also increase the strip’s reusability,” she says. She hopes to see her innovation being deployed around the world, and the eventual use of this harvested algae in the making of biofuels.
In 2022, Moitri also placed second in the technology category at the Broadcom MASTERS, taking home a cash prize and the opportunity to attend a STEM summer camp. She decided to follow her interest in medicine and medical university at the University of Connecticut’s Pre-College Summer Program for its pre-med focus. There, she spent her time attending lectures in the morning and taking practical lessons in the afternoons, exploring a different specialization everyday. “using mannequins, we did simulations of emergency situations,” says Moitri, who has always been fascinated by the human body and its many complex functions.