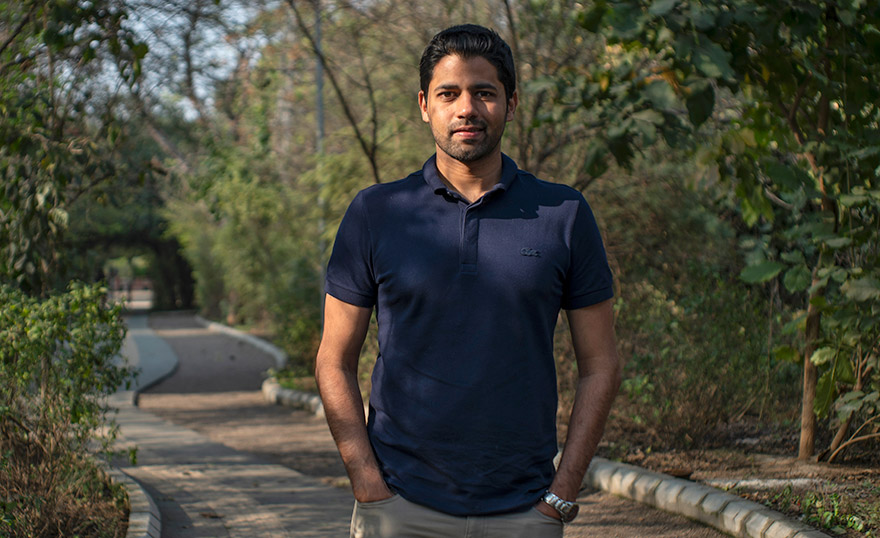
(August 28, 2024) In 2021, at the age of 16, Snehadeep Kumar spent the lockdown trawling Discord, looking for like-minded people to join his space tech startup. At the time, the teenager’s mission was to build the world’s smallest telescope. Three years later, he has altered his goal, but his mission remains the same – to stay on the frontiers of cutting-edge space research. Snehadeep is the co-founder of the Nebula Space Organization, a Fellow of the Royal Astronomical Society, an Honorable Kentucky Colonel and a Young Member of the New York Academy of Sciences. The Nebula team is currently working on building India’s first gamma base cube sat.
Cubesats are a class of nanosatellites, usually measuring 10x10x10 cms. Now, the development of CubeSats is an industry unto itself, as they provide a cost-friendly platform for scientific investigations. “Satellites usually cost anywhere between $75 million. A CubeSat reduces costs by about 90 percent,” Snehadeep tells Global Indian, holding up a model of a CubeSat to demonstrate. In 2010, ISRO launched the AstroSat, built with a budget of $50 million. The satellite, which was roughly the size of a room, was searching for gamma ray bursts to understand how black holes are formed. “Now, we’re attempting to do the same thing with a CubeSat, which will cost only Rs 10 lakh,” he explains.
The Nebula team has developed a proof of concept, which they have presented at ISRO. “We were one of two CubeSat based teams selected by ISRO for the National Space Science Symposium,” Snehadeep says. They have also been selected to attend the International Astronautical Congress 2024, to be held in Italy this year.

Snehadeep Kumar, co-founder, Nebula Space Organisation, is attempting to build the smallest CubeSat
For over a decade, ISRO has been supportive of students in space tech, and welcomed their innovations. In 2010, ISRO launched STUDSAT, a CubeSat designed by students. The project had been conceptualised and executed by undergraduate students across the country. The picosatellite was launched on July 12, 2010, from the Satish Dhawan Space Centre. At the time, the objective was for students to get hands-on experience in space missions, and they were given autonomy with the design and fabrication of the picosatellite. It was also the smallest satellite launched indigenously by an Indian organization.
Growing Nebula
What started as an online group has come a long way. “When I started in October 2021, I had to work with an online team, but it’s not possible to run a space tech startup that way,” Snehadeep admits. At the time, they wanted to build the world’s smallest, functional space telescope, and were also studying the Milankovitch Cycles (changes in climate caused by the Earth’s movements).
His fortunes changed when he began his undergrad, at the Kalinga Institute of Industrial Technology in Bhubaneswar. There, he had the opportunity to build a team, and also met Mohit Kumar Nayak, who is the Managing Director of Nebula. “I have always wanted to explore space and space tech, since my childhood days when I would spend nights in my father’s village in Odisha looking at the stars,” says Mohit. Now, he’s responsible for growing the business itself, and spends his time attending conferences and networking with potential investors.
“Nebula is in the growing phase, we have done the theory and the research and we are preparing for the assembling and manufacturing part,” Mohit explains. Their aim is to begin building the protype in October 2024, which will go through three rounds of testing.
“The first round of testing is with a hydrogen balloon. Then the prototype will be sent to a private testing unit. The third phase is approaching bigger agencies who can deploy our satellite in outer space,” Snehadeep explains.
When science caught his fancy
Snehadeep’s talent for science surfaced early – by the age of eight, in fact. His parents, keen to stoke his curiosity, subscribed to several student newspapers like Times NIE, which he read cover to cover. “I would read about science and scientific experiments and be completely fascinated by it all, also films like Interstellar and Inception, and Christopher Nolan’s Tenet inspired me,” says the Indian teen scientist. His father works at SAIL, and his mother is a homemaker.


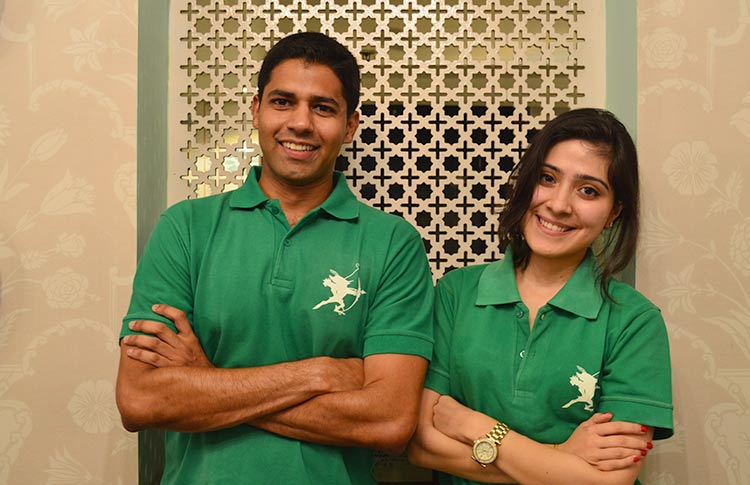
The Nebula team
In third grade, an astute science teacher at his school DAV Model School, Durgapur, Soma Ghosh, noticed Snehadeep’s inclinations and took it upon herself to encourage him. “She asked me to participate in a science competition – Intel IRIS,” says the lad who grew up in Durgapur, Bengal. With her help, he built a functioning electromagnetic circuit, connected to a bell. “She taught me how to conduct a project, and write about it,” he adds. In Class 9, another mentor, Sushmita Chandra, a science teacher, cemented his knowledge – he worked on three projects with her.
That year, he began looking into trapping excess water from the soil. “Roots don’t absorb all the water, so where does the rest go? Can we save it? I placed a device that comprised a filtration tank, and a containment tank – water goes into the container, then into the filter for purifying,” says the Indian teen scientist, of the filtration tank which contained moringa seeds, a natural purifier. “We tested the water, and it was fit to drink. SRM University funded the project. I also began thinking of publishing this in a journal,” he adds. Another project involved creating electricity out of carbon monoxide released from cars – creating a rechargeable hybrid battery.
The perils of publishing
Getting published is tough, the Indian teen scientist found out. He approached Nature.com and Scientific American, and was turned down. “I also learned that we need to pay to have our articles published. Besides, journals like Scientific American accept submissions only from PhD candidates, or people with undergraduate degrees,” the Indian teen scientist says.
By this time, Snehadeep was already in communication with some of the world’s top scientists – Dr Tom Welton, president of the Royal Society of Chemistry, London and the Nobel Prize-winning physicist Gerard ‘t Hooft, who, “likes to chat with students. He would send me practice papers to solve,” smiles the Indian teen scientist, adding, “I have always been interacting with scientists, Nobel Laureates, to discuss problems in maths and physics.”


Always on the lookout for new programmes to do, new things to learn, normal teen activities are much too passe for him. “I received an acceptance from the Oxford summer programme but won’t be able to attend because of dates,” he mulls. The Indian teen scientist is also part of the Asteroid Search by Nasa’s Astronomers Without Borders, an initiative through which citizen scientists get the chance to make original astronomical discoveries.
Snehadeep’s achievements:
- Received a Rs 56 lakh scholarship from Lifology, to pursue a bachelor’s degree from select universities across the world.
- Top 10 from India by Environcentre Foundation in 2021, for his project “Coagulated water filter and purifier.”
- Silver medal in the SRM University Mission Invention. The country’s biggest science fair
- A Young Fellow of Harvard’s CYES. The Harvard’s Entrepreneurship Society, with a very selective procedure
- Immerse Education Cambridge Summer Camp in 2020 and Oxford Summer Camp in 2022
- A young member of the prestigious New York Academy of Sciences, which selects 1,000 students from over 2 million entries.
- Follow Snehadeep Kumar on LinkedIn