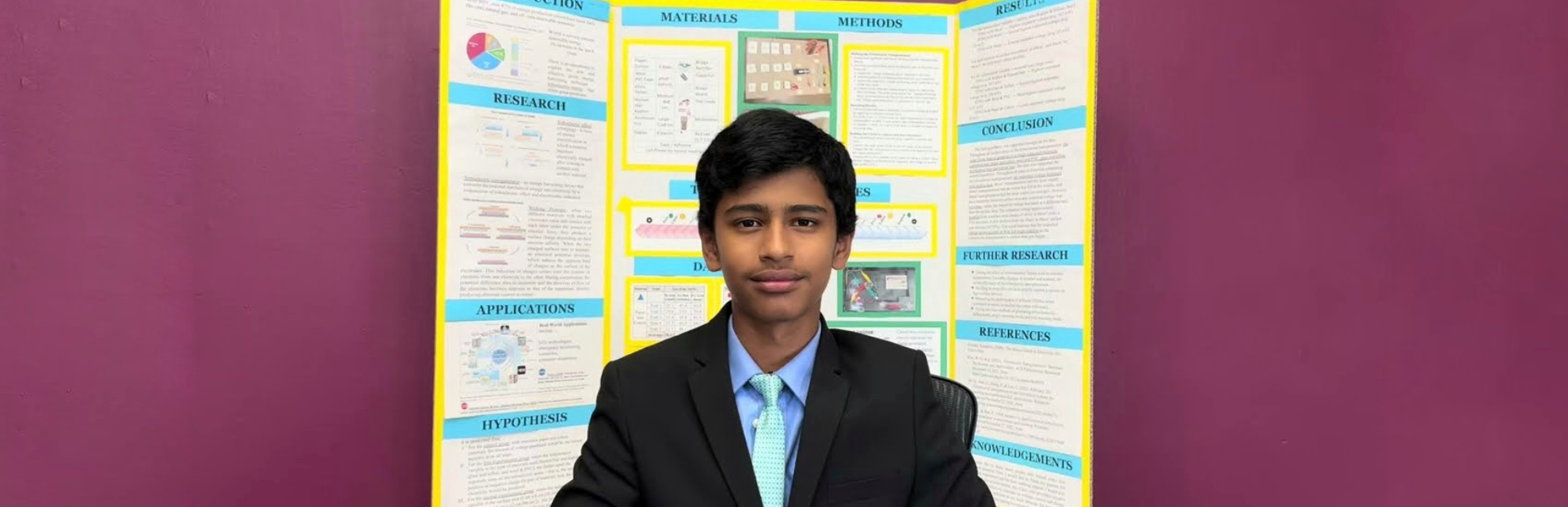
(December 2, 2023) Often sparked by dry weather, strong winds, or human actions, wildfires have been wreaking havoc on our forests where countless plants and animals thrive. Sadly, the increasing number and strength of wildfires are putting vital ecosystems at risk, endangering the web of life that relies on them. While these fires have become very common in various parts of the world, Adyant Bhavsar’s hometown California has seen some terrible wildfires over the last few years. And that is what motivated this seventh-grade innovator to design a machine that could convert waste mechanical energy into electricity through triboelectrification and electrostatic induction.
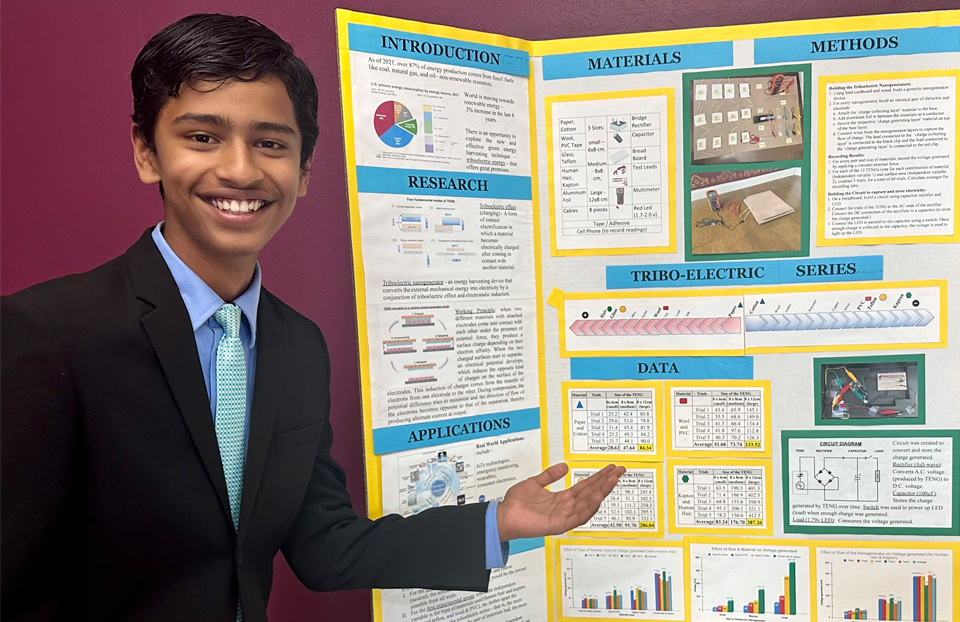
“California has been rocked by several devastating wildfires over the years, and thus the state has hundreds of cameras and sensors set up to monitor wildfires and other disasters. This got me thinking,” the innovator said during a recent interview, adding, “To increase the reliability, these devices would need a sustainable energy supply that does not need frequent recharging or replacing.” In his search for renewable energy options, Adyant stumbled upon something called a triboelectric nanogenerator. This gadget turns mechanical energy into electricity. When two thin, adjacent objects move apart or rub against each other, electrons move between them, creating an electric charge.
For this brilliant idea, the Global Indian recently won the Lemelson Award for Invention, at the Thermo Fisher Junior Innovators’ Challenge (JIC), 2023. “My equipment is a novel invention that uses a nanogenerator to increase sustainability and reliability. This competition gave me a great confidence boost and encouraged me to continue striving towards greatness. I am most excited about the challenges and want to work together with fellow like-minded peers to be able to solve some real-world problems,” says the innovator who also won a prize amount of $10,000 along with the award.
Not just a science guy
Raised in San Jose, California, Adyant has consistently demonstrated academic excellence. Although aspiring to pursue a career in the sciences, this young innovator’s true passion lies within the pages of books. An avid reader, Adyant started reading when he was just three years old. By six, he had finished reading the Harry Potter series and many of the Magic Tree House and Box Car series books. Interestingly, the innovator is the author of a children’s fantasy fiction book, The Mystery at Beartown Campsite.


Mostly busy with his science projects and experiments, Adyant enjoys reading, writing, piano, basketball, tennis, speech, and debate, during his free time. “These hobbies enable me to express myself, gain diverse perspectives, and positively influence others with my ideas,” said the innovator, who has also won several writing awards. The youngster wishes to become an environmental engineer. “I want to contribute my skills toward finding solutions for environmental challenges, such as deforestation and pollution. I plan on trying to implement the sustainable generator that I invented in more places worldwide and to reach out to people, who are working on the same technology across the globe, to help drive the ship away from fossil fuels and towards more renewable resources,” he said.
Saving the environment
After doing weeks and weeks of research about his experiment on his “waste to wattage” project, the innovator first built his own triboelectric nanogenerator, by placing two wooden planks together with springs in between. The innovator assembled each plank with layers of various materials connected to electrodes. These material pairings encompassed glass with Teflon, Kapton with human hair, wool with PVC, and paper with cotton. Adyant conducted five trials for each combination, pressing the top plank to bring the material layers into contact.


As the materials touched and separated, they exchanged electrons, resulting in an induced current. Adyant also varied the surface area for each material pairing, discovering that Kapton, an electronic film paired with human hair, generated the most electricity. Increasing the surface area for all materials led to a linear growth in electrical output. Additionally, the innovator incorporated a capacitor into the circuit to store the generated electric charge, successfully accumulating enough energy to power a 1.79-volt light-emitting diode (LED). “This triboelectric nanogenerator is lightweight, low-cost, eco-friendly, and customisable,” the innovator explained, adding, “Figuring out how to amplify to power high-voltage electronics would further optimise my triboelectric nanogenerator. I might also try connecting several of them and explore other methods of generating triboelectricity.”
- Follow Adyant Bhavsar on Twitter




